Friday, July 18, 2008
A Simple Guide to Hyperhidrosis
---------------------------------
What is Hyperhidrosis?
----------------------
Hyperhidrosis is the condition when a person suffers from excessive perspiration due to overactivity of the sweat glands.
This may cause a social problem in people who need to shake hands or write with sweaty palms.
Excess perspiration with foul odor may also be offensive to people around the patient
What are the causes of Hyperhidrosis?
---------------------------------------
The cause of Hyperhidrosis is usually unknown.
It has been linked to :
1.excessive sweat glands
2.psychogenic excess production of sweats under stress and nervous conditions
3.Endocrine disorder such as hyperthyroidism
4.Skin diseases with increased hydration of skin such as in weeping eczema
5.Genetic - inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Family has a history of Hyperhidrosis
6.diseases of the nervous system
7.Tuberculosis-night sweats are a typical feature of tuberculosis
8.diabetes mellitus and pituitary disorders
9.Certain medicines such as aspirin, paracetamol may provoke excess sweating
10.alcohol, caffiene, and certain food(spices) may stimulate the sweat glands
What are the symptoms and signs of Hyperhidrosis?
-------------------------------------------------------
Persons who has Hyperhidrosis has the following:
Symptoms:
1.Genralised sweating
2.localised sweating of palms, soles, axilla and groins
3.Foul smell from the excess sweat is caused by the decomposition of skin cells by bacteria and yeast infection
Signs:
1.Skin may become thickened, fissured or scaly
2.Nail deformities may occur
3.Secondary bacterial and fungal infections may be present
How do you diagnose Hyperhidrosis?
-------------------------------------------
Diagnosis can usually be made by :
1.Sweaty palms or soles
2.thickened, fissured skin with nail deformities
What is the treatment of Hyperhidrosis?
------------------------------------------------
1.Treat the underlying cause such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes
2.Clean involved skin frequently with baths etc. Use talcum powder to dry skin.
3.Wear cotton socks and underwear and change daily.
4.Local application of aluminium chloride, hexahydrate, glutaradehyde and even tannic acid from tea.
Some side effects may be allergic dermatitis or staining of skin
5.Anticholinergic drugs can reduce the sweating but has side effects such as dryness of mouth and flushing
6.Surgery in severe cases may be required such as sympathectomy (for palms).
Sweat glands suction by removing some of the sweat glands has been shown to reduce sweating
7.Iontophoresis: may help but may be painful
8.Botox injection may disable the sympathetic nerves to the sweat glands amy lasts for 6-9 months
9.Hypnosis, relaxation and meditation has help to certain extent
10.Radiotherapy has been known to be effective but not used because of the danger of bone cancer.
What is the prognosis of Hyperhidrosis?
----------------------------------------
Prognosis is usually palliative as the sweat glands and nerve cells may grow back.
Recurrence is quite common.
Monday, June 9, 2008
A Simple Guide to Coughing
------------------------------
What is Coughing?
----------------------
Coughing is the reflex mechanism in which the body tries to get rid of excessive mucus and phlegm accumulated in the lining membranes of the respiratory tract.
The secretions from the lining of the respiratory tract trap and then flush out the viruses, bacteria and other particles like smoke, haze particles.
It prevents serious infections from entering the lungs and bronchial tubes.
What are the common causes of cough?
---------------------------------------
Coughing is usually caused by the following:
Infections:
1.bacterial or viral infection of the nose and throat such as the common cold or influenza.(yellow or green phlegm)
2.anaerobic infections of the mouth,
3.Infection of the tonsils, nose and sinuses(postnasal drip)
4.Bacterial infection of the bronchial tubes and lungs(bronchiectasis, bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, or tracheitis).
This often comes with rusty or green mucus.
Dry mouth:
1.Insufficient drinking of water
2.medications especially ACE inhibitors(eg. enapril) can cause dry persistent coughs
Allergies:
1.Certain plants, pollens, chemicals, cosmetics can cause allergic reactions in the throat and bronchial causing cough. (white clear phlegm)
2.Asthma - narrowing of the bronchial tubes due to allergic and other causes usually results in white sticky clear productive phlegm
Smoking:
Cigarettes smokes contains 40 over chemicals which irritates the cells in the lining of the bronchial tubes causing a chronic cough
Stress:
Stress can cause cough due to dryness of mouth during stress or anxiety, causing the saliva to dry up and producing dry unproductive cough.
The cough in stress usually disappears during sleep.
Gastric problems or indigetions
1. Indigestion of food in the stomach can cause the undigested food in the stomach to produce gas in the stomach which goes upwards to the throat drying saliva which then become irritating phlegm in the throat.
2.gastroesophageal reflux of food can also cause the acid and undigested food to travel to the mouth and produce mucus secretions.
Systemic diseases:
1.Congestive heart failure
2.Lower respiratory tract infections
3.Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
4.Carcinoma lung.
What investigations are needed for cough?
------------------------------------------
1.chest X-ray
2.sputum culture
3.pulmonary function tests
What is the treatment of Coughing?
-------------------------------------
Medications
1.Approprate Antibiotics, antifungal for infections of throat and bonchial tubes
2.Antihistamines for allregic cough
3.Bronchodilators for asthma and Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
4.cough mixtures - expectorants helps to expel out the phlegm
- suppresant suppress the cough -especially for dry cough and at night to stop the cough
5.Antacids and antiflatulent agents to get rid of gas in stomach and prevent reflux
6.Diuretics for treatment of congestive heart failure especially in the elderly
Healthy Lifestyle:
1.drinking several glasses of water a day prevents dryness of mouth
2.Avoid cold, acidic, spicy and oily food which irritates the throat
3.Proper oral hygience after eating: brushing of teeth and flossing.
4.Gargle mouth after every meal.
4.Avoid smoking
6.Avoid frequent usage of the voice and throat - do not talk too much
6.Treat underlying condition such as asthma, diabetes, liver, kidney and other conditions.
Tuesday, May 27, 2008
A Simple Guide to Urinary Incontinence
------------------------------------------------
What is Urinary Incontinence?
----------------------------------------
Urinary incontinence is a symptom and means the the uncontrollable leakage of urine.
It can cause a lot social discomfort to patients having this problem.
Men are more prone to it than women.
What are the Causes of Urinary Incontinence?
------------------------------------------------
Urinary Incontinence is a medical condition which may be temporary or permanent.
There are many causes of urinary incontinence:
Temporary urinary incontinence
------------------------------
1.Drinking too much tea, coffee or carbonated drinks can irritate the bladder and cause or contribute to incontinence.
Coffee and other drinks containing caffeine can be a particular problem as caffeine is a diuretic, i.e. it increases the urge to pass urine.
2.Excessive alcohol. Alcohol is also a diuretic. Because it has deppresant effect on the the brain, it may affect the person's judgement temporarily, hence resulting in accidental leakage of urine.
3.Some medications like diuretic pills, heart medications and antidepressants can cause or contribute to incontinence.
4.Urinary Tract Infection may cause sufficient irritation to the bladder to stimulate incontinence.
5.Constipation result in impaction of the stools in the rectum. This irritates the nerves to the bladder resulting in incontinence.
Permanent urinary incontinence
-------------------------------
In both sexes there are many conditions which can cause or contribute to chronic or persistent urinary incontinence:
1.Aging
With age there is a decrease in the bladder capacity to store urine.
2.Enlarged prostate in men
BPH or benign prostatic hypertrophy is associated with aging and can obstruct the urethra and block urinary flow resulting in urge or overflow incontinence.
3.Prostate Cancer in men
Prostate cancer can cause incontinence if untreated. However the incontinence in prostate cancer patients may be a side effect of treatment e.g. surgery, radiation therapy.
4.Prostatitis in men
Inflammation of the prostate gland sometimes can cause constriction of the urinary flow and incontinence.
5.Gynecological problems such as prolapsed uterus, enlarged utrue due to fiboids, ovarian cysts or tumours can pulled on the muscles of the perineum causing weakness of the muscles and poor constriction of the bladder opening
5.Surgery involving the organs near the bladder
Any operations involving organs such as the ovary, uterus, prostate, rectum can cause inadvertent damage to muscles or nerves of the urinary tract, resulting in incontinence.
6.Urinary tract obstruction
Any enlarged tumours along the urinary tract can obstruct the normal flow of urine and cause incontinence. Bladder stones can do the same.
7.Neurological conditions
Stroke, Parkinson's disease, tumours in the brain or spinal cord and injury to the nerves in pelvis or spinal cord can can affect the nerves to the bladder and weakening of the bladder opening muscles.
What are the Types of urinary incontinence?
-----------------------------------------------
Urinary incontinence may be categorised into 4 main types. It is possible however to have more than one type of urinary incontinence
1.Stress incontinence
Leakage of urine occurs because of weakness of the pelvic floor muscles. When there is pressure exerted on the bladder - e.g. from laughing, sneezing, coughing, exercising or heavy lifting, pregnancy, the muscles at the opening of the bladder comes under stress and opens to allow leaking of urine.
2.Urge incontinence
There is an uncontrollable leakage of urine while suddenly feeling the urge to urinate.
3.Overflow incontinence
There is a constant dribbling of urine even after finishing urination. There is an inability to completely empty the bladder.
4.Functional incontinence
There is physical or mental impairment resulting in the failure to realise the need to urinate.As a result the person fail to get to the toilet in time and pass out the urine. Examples are people who suffer from dementia, parkinson or is incapacitated by poor physical movement.
Other types of urinary incontinence include enuresis(bed wetting ) which is common in chilldren,
Transient incontinence which is temporary and sometimes caused by medications.
What are the symptoms of urinary incontinence?
------------------------------------------------
The main symptom of urinary incontinence is leakage of urine. This leakage may be frequent and heavy, or it may be small and rare.
Some other symptoms of urinary incontinence include:
Urgency - a strong desire to urinate even when the bladder is not full together with pelvic discomfort or pressure
Frequency - urinating more than once in a two-hour period or more than seven times a day
Nocturia - the need to wake up and urinate at least twice during sleep
Dysuria - painful urination
Enuresis - bed-wetting or urinating while sleeping
How do you make the Diagnosis of urinary incontinence?
----------------------------------------------------------
1. history taking is important especially the pattern of urine leakage. Other history include symptoms of straining and discomfort, use of drugs, surgery, and illness.
2. physical examination will look for signs of medical conditions causing incontinence, such as pelvic tumors, stool impaction, and poor reflexes or sensations.
3. measurement of bladder capacity and residual urine for signs of poor functioning bladder muscles.
4.Stress test - the patient coughs vigorously as the doctor watches for loss of urine.
5.Urinalysis - urine is tested for infection, urinary stones.
6.Blood tests - for PSA( in case of Cancer of prostate) or alphafoetoprotein (in case of cancer of the ovaries)
5.Ultrasound -to visualize the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
6.Cystoscopy - a thin lighted tube is used to see the inside of the urethra and bladder.
7.Urodynamics - measurement of pressure in the bladder and the flow of urine.
What is the Treatment of urinary incontinence?
-----------------------------------------------
Elderly patient tend to believe that the only way to prevent embarrassment is to wear absorbent pads or padded undergarments like adult Pampers. However the wetness may lead to rashes, sores, or infections.
Treatment involves:
A. making certain lifestyle changes.
1.Timed Voiding
Timed voiding (urinating) means writing a chart of your urination and leakage patterns for several days. This will then tell you which times of day you normally need to empty your bladder before leakage may occur.
2.Bladder training
This involves training your bladder to control the urge to urinate.
3.Changing Fluid Intake
Restricting your fluid intake, or changing the timing of fluid intake will help you to gain more control over the bladder. Restriction of alcohol, tea, coffee and other caffeinated beverages can reduce the amount of urine from your body
4.Exercises
Exercising the muscles of the pelvis(Kegel exercises) may strengthen the muscles of the affected area.
5.Vaginal cone therapy
This exercise for women involves the use of a set of five small vaginal cones of increasing weight. The patient simply places the small plastic cone within her vagina and hold it in by a mild reflex contraction of the pelvic floor muscles. This exercise is done twice a day for fifteen to twenty minutes.As the pelvic floor muscles becomes stronger, cones of increasing weight can be used, thereby strengthening the muscles gradually.
6.Electrical stimulation
Electrodes are temporarily placed in the vagina or rectum to stimulate nearby muscles and strenthen the pelvic muscles.
This can reduce stress and urge incontinence.
7.Biofeedback
Using electronic devices or diaries to track when the bladder and urethral muscles contract, the patient can slowly control movement of these muscles.
B.Treating the cause of the incontinence:
1.Medications:
drugs may be given to treat urinary tract infections or inhibit contractions of an overactive bladder.
2,Pessaries
A pessary is a ring shaped medical device that is inserted into the vagina. It compresses the urethra against the pubic bone and elevates the bladder neck.
3.Surgery
Surgery to reduce the size of your prostate gland ( transurethral resection of the prostate or TURP) helps to reduce urinary incontinence in men.
Bladder repositioning
In older women incontinence results from the bladder dropping down toward the vagina. Surgery involves pulling the bladder up to a more normal position. Using an incision in the vagina or abdomen, the surgeon raises the bladder and secures it with a string attached to muscle, ligament, or bone.
Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz
This procedure also known as retropubic suspension or bladder neck suspension surgery, is performed using an incision across the abdomen. Stitches are placed in these tissues near the bladder neck and the urethra is then lifted, and the stitches are attached to the pubic bone or to tissue behind the pubic bone. The bladder neck is supported helping the patient to control the urine flow.
Slings
The sling procedure uses synthetic mesh material in the shape of a narrow ribbon that is placed under the urethra through one vaginal incision and two small abdominal incisions. The purpose is to provide support under the urethra. There are the Transobturator Tape Sling, the Tension-free Transvaginal Sling, and the Minisling.
Artificial urinary sphincter
Rarely the surgeon implants an artificial urinary sphincter a doughnut-shaped sac surrounding the urethra. To close the urethra A fluid fills and expands the sac. Pressing a valve implanted under the skin, the artificial sphincter can be deflated allowing urine from the bladder to pass.
4.Catheterization
A catheter may be inserted to drain the urine if your bladder never empties completely or if your bladder cannot empty because of poor muscle tone, post surgery or spinal cord injury. This can be done on a if required basis.Prolonged catherisation may lead to infection of the urinary tract.
5. Botox injections
Botox injection has been tried to reduce the sensitivity of the nerves at the opening of the bladder. It appears more successful for women than in men.
How do you prevent urinary incontinence?
----------------------------------------
Reduce your risk of urinary incontinence:
1.Maintain a healthy weight.
2.Obesity can lead to urinary incontinence.
3.Avoid constipation by drinking sufficient amounts of fibre and fluids in your diet.
4.Avoid drinks which can irritate your bladder such as coffee, tea, carbonated drinks and alcohol.
Friday, April 4, 2008
A Simple Guide to Erectile Dysfunction
-------------------------------------------
What is erectile dysfunction (ED)?
----------------------------------------
Erectile dysfunction is defined by the WHO as "the consistent or recurrent inability of a man to attain and/or maintain a penile erection of the penis sufficient for sexual performance"
The WHO sponsered Consultation recommend" a minimum of three months of erectile difficulty qualified foe a diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction."
What is the incidence of ED?
-----------------------------------
The incidence of ED is unknown:
ED is currently underdiagnosed and undertreated.
More than 50% of all men 40-70 years old are likely to experience it.
What are the Causes of ED?
----------------------------
Erectile dysfunction can be due to:
1.Medical causes
2.Lifestyle causes
3.Psychosocial causes
4.or a combination of these.
Medical causes:
------------------
1.vascular disease-is the most common cause of ED.
atherosclerosis(hardening of the arteries)
high blood pressure
high cholesterol
heart disease
stroke
All these conditions affects the blood flowing and out of the penis.
2.diabetes-
can cause nerve damage and damage to the blood vessel to the penis resulting in two thirds patients developing ED
3.nerve disease-
such as spinal cord disease, nerve degeneration from diabetes and alcohol can reduce the sensitivity of the nerves to the penis
4.hormonal problems-
low levels of testosterone(male hormone) can cause ED
5.Surgery-
any surgery of rectum,colon or prostate cancer and radiation therapy in the genital area may damage nerves and blood vessels to the penis.
6.Trauma-
spinal cord injury and pelvic fractures damages the nerves and blood vessels to the penis.
7.Side effects of medications (e.g. certain high blood pressure medications, antidepressants,tranquillisers) may reduce the blood flow to the penis
8. Urinary infections and a disease called Peyronie's Disease(causing scar tissue in the penis) can cause ED.
Lifestyle causes:
----------------------
1.alcohol -
heavy drinking reduces the ability to have a strong erection. long term excessive drinking damage nerves and blood vessels to the penis.
2.Smoking-
The incidence of ED in smokers are hiher than in non smoker because the toxic chemicals in the cigarettes can damage nerves and blood vessels to the penis.
3.Substance abuse such as heroin etc can cause damage to the nerves and blood vessels to the penis.
4. Sedentary lifestyle-
Lack of exercise may lead to ED due to poor blood circulation
Psychosocial Causes:
-----------------------
1. Performance anxiety -nervousness and worry about poor sexual performance
2. Stress due to any cause
3. Depresssion
4. Relationship Problems- marital problems and tensions may affect sexual relationship
5. fatigue.
How is the diagnosis of ED made?
---------------------------------
1.medical hisory especially about diabetes, hypertension, medications, alcohol adrug abuse,smoking.
2.medical examination including genitals and prostate
3. Blood tests of testosterone, cholesterol, sugar and PSA( in males above 50)
What is the treatment of ED?
------------------------------
Successful treatment of erectile dysfunction includes:
1. Lifestyle modifications:
exercising
dieting
quitting smoking
reducing alcohol/drug abuse
counselling to manage anxiety/stress/marital problems
2.treatment of underlying medical conditions such as diabetes
3.change of medications
4.medication for treatment of ED.
There are now oral medications available to treat erectile dysfunction.
They belong to a group of drugs known as phosphodiesterase inhibitors
e.g. Viagra, Cialis, Levitra.
There is no instant erections when the medicine is taken but with physical and psychological stimulation erections do occur.
Most of the men who has taken the drugs have had improvements in their erectile functions regardless of the cause of the ED.
Certain patients with heart problems or a history of stroke are advised against taking medications belonging to this group.
6.Other treatments for erectile dysfunction
a.Penile Injection therapy- medication which increases the blood flow in the penis is injected into the penis to cause erection before sexual activity
b.Intrautrethral therapy -pellets of medications which increases blood flow is inserted into the urethra which is the tube from the bladder to the outside.
c.Vacuum therapy :
This procedure holds the blood in the penis using a ring at the base of the penis
d:surgery for blocked blood vessels
e.penile implants -these are inserted into the penis and inflated when there is a desire for sexual intercourse.
This surgery is offered when all other options failed.
How to cope with ED?
-----------------------
Erectile dysfunction can cause a lot of stress on one’s marital relationship.
Communication and honesty with the spouse is important in ED.so that she understands the problem and that she is not the cause of the problem.
In recent years, more men are becoming aware of the treatment of erectile dysfunction and are seeking help.
Tuesday, February 12, 2008
A Simple Guide to Cervical Spondylosis
---------------------------------------------
What is Cervical Spondylosis?
----------------------------------
Cervical Spondylosis is a degenerative disease of the joints of the cervical spine(neck), causing pain in the neck and nerve root irritation.
Who get Cervical Spondylosis?
-------------------------------------
Every one can get Cervical Spondylosis.
The age of onset is usually in the late 40 or early 50.
It is also more common in men than women.
It is worst in the lower cervical spine.
What are the causes of Cervical Spondylosis?
-----------------------------------------------
The causes of Cervical Spondylosis are:
1.Age Degeneration of the cervical spine due to usage such as bending the head to read or write.
The weight of the skull also serves to compress the vertebrae of the cervical spine as well as the intervertebral discs causing narrowing of disc space and bone protrusions called osteophytes which becomes worse with age.
2.Trauma and injury such as whip lash injury, head injuries can also indirectly injure the vertebra of the neck and cause intervertebral disc protrusions.
3. Congenital abnormality of the cervical spine such as incomplete formation of the vertebra and disc.
What are the Symptoms of Cervical Spondylosis?
-------------------------------------------------------
1.The onset is usually gradual with occasional neck pain over weeks or months.
2.There may be a history of trauma to the neck or prolonged neck strain.
3.Early morning neck stiffness and pain may occur,then wears off during the day.
4.The pain may radiate to the shoulder or upper limb.
Pain can be persistent in some cases.
5.Numbness, paresthesia even weakness of the arm and hands may occur due to compression of the neck nerve root.
6.Headaches may be common due to pressure on the neck muscles giving rise to pain to the occiptal region.
7.Neck movements may be restricted in all directions. There may be creaking sounds of the neck on movement.
8.Muscle weakness of the upper and/or lower limb with muscle wasting
Pain may be aggravated by stress, poor general health, prolonged period of the neck in one position.
How is Cervical Spondylosis diagnosed?
-----------------------------------------
Confirmation is usually by an xray of the cervical spine which may show:
Typical cervical vertebra degeneration,
Disc space narrowing
Osteophytic changes
Narrowing of the exit foramina
Subluxations of the vertebra
Sclerosis of the vertebral margins
Lordosis of the spine
How to treat Cervical Spondylosis?
------------------------------------
Not every patient suffer the same degree of symptoms
1. mild requiring only exercises or mild pain killers.
2. more severe require:
a.Neck collars
b.physiotherapy -cervical traction, shortwave diathermy, neck exercises
c.NSAIDs painkillers
d.surgery for cord compression,intractable root symptoms,vertebral artery compression,weakness of arms or legs
3. All cases require:
protection of neck from muscle strain
avoidance of excessive bending and turning of neck
maintenance of good posture
avoidance of emotional stress
What is the prognosis of Cervical Spondylosis?
------------------------------------------------
Symptoms comes and go.
With exercise and NSAIDS, pain is reduced and flexibility of the spine is improved especially with regular exercise and proper posture.
Injury and stress can aggravate the condition.
There is no cure.
Saturday, November 3, 2007
A Simple Guide to Headache
A Simple Guide to Headache
---------------------------------
What is Headache?
----------------------
Headache is a very common complaint, not an illness.
It literally means pain in the head.
What are the Common Types of Headaches?
--------------------------------------------------
Tension headache:
-----------------
as defined by the International Headache Society is characterised by:
1.bilateral location
2.pressing/tightening (non-pulsating) quality
3. mild to moderate in intensity
4. not aggravated by routine physical activity like walking or climbing stairs.
It is the most common headache and may be associated with contractions of head and neck muscles due to physical or mental stress. The headache is made worse by changes in the environment, drugs, or factors unique to the individual.
It can also be classified into 2 side types:
episodic (<>
chronic (> 14 days a month on average and <>
Treatment can be divided into:
pharmaceutical
non pharmaceutical
Pharmaceutial:
can be divided into acute and prophylactic.
In acute treament simple painkillers is usually effective.
In prophylactive treatment,antidepressants like amitriptyline usually help in the prevention of tension headache.
Medicines should always be given at low doses and titrated up to therapeutic doses to minimise side effects.
Non-pharmaceutical:
1. rest
2. removal of aggravating factors.
3. relaxation exercises
Migraine:
-----------
is defined as a heavy throbbing pain usually over one side of the scalp, forehead and about the eye, caused by abnormally dilated blood vessels.
Migraine may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting or sensitivity to loud noises or bright lights.
It is also triggered by certain factors unique to the individual such as:
1.menstruation,
2.alcohol,
3.anxiety,
4.loud noises,
5.bright lights
A validated 3 items questionaire covering
1. disability
2. nausea
3. sensitivity to lights
should given to every patient to screen the severity of the migraine.
Treatment again is divided into:
phamaceutical
non-pharmaceutical.
Pharmacetical:
can be divided into acute and prophylactic.
In acute treament simple painkillers like paracetamol is usually effective in mild cases.
Non-steroidal anti-inflamatory drugs should be tried if paracetamol fails.
If NSAIDs are ineffective then migraine-specific drugs like triptans or ergotamine which act to constrict blood vessel should be tried.
In some cases anti-emetic drugs like stemetil to prevent vomiting is given together with the migraine medication.
In prophylactic treatment, the goals are to:
1. reduce frequency,severity and duration
2.improve function and reduce disability
3.improve responsiveness to treatment of acute attacks
Medicines used include:
betablockers
Calcium channel blockers
Serotonin receptor antagonists
Antidressants
Anticonvulsants
Angiotensin blockers
NSAIDs
Non-pharmaceuticals:
1.resting in a cool, dark and quiet room.
2.relaxation exercises
3.Solving the triggering factors also help.
4.Oestogen containing oral cotraceptives should avoided in menstrual migraine.
During pregnancy or lactation treatment should be non-pharmaceutical when possible. If necessary paracetamol is the safest drug for women during pregnancy or lactation.
Cluster headaches
----------------------
is defined as pain which occurs in runs with tearing pain over the forehead or behind the eye(s) with flushing of the face.
There are aura of stars,flashing lights etc associated with this headache.
The cause is beleived to be due to histamine release from ingestion of certain foods like cheese, seafood,alcohol etc.
It is more common in males.
Treatment is by
1.strong painkillers
2.avoidance of food triggers
3.rest.
What are Secondary headaches?
---------------------------------------
It is diagnosed by its close relation to a disorder that is known to cause headache.
The headache improves or disappear after successful treatment or spontaneous resolution of the causative illness.
1.Sinus headaches:
----------------------
are due to acute sinus inflammation attacks.
Pain is over the frontal forehead and the upper cheeks.
It may be associated with fever and heavy mucus production.
Treatment is by
1.antibiotics for the sinus infection,
2.antihistamines to reduce mucus production
3.painkillers
4.rest.
2.Referred headaches:
---------------------------
these are caused by by referred pain from disorders of structures around the head. Common ones are
1. earaches,
2. toothache causing pain over an entire part of the face and
3. temporomandibular joint dysfunction from mechanical pain from the jaw joint.
4. temporal arteritis, a rare inflammatory blood vessel condition causing persistent headache at the temporal artery. There is possible complication of blindness secondary to anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. The headache usually resolves or improves with 3 days of high dose steroid treatment.
3.Meningitis / Encephalitis headaches:
---------------------------------------------
caused by infection of the brain tissue (encephalitis) or the membranes surrounding the brain (meningitis).
Headache is the most common symptom. The pain is diffuse and progressive with fever, a painful stiff neck and other symptoms such as drowsiness, seizures and neurological problems including weakness and numbness.
This type of headache needs immediate hospital treatment.
4.Cerebrovascular Accidents (haemorrhagic stroke):
-------------------------------------------------------------
a stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked or bursts.
Bleeding in the brain causes a sudden severe headache.
There is also associated loss of consciousness and other neurological signs such as weakness, numbness and seizures.
This type of headache needs immediate hospital treatment.
5.Brain Tumour:
------------------
is rare and causes a gradual headache lasting for weeks.
It is localised and associated with nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and loss of weight.
It is worse in the morning and aggravated by coughing or leaning forward.
By the time neurological symptoms appear such as seizures, numbness, weakness or blindness, the brain tumour has already grown to an advanced stage.
Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
6. Other causes of secondary headaches are:
a.post traumatic headache following a head injury
b.whiplash injury
c.cerebral venous thrombosis
d. idiopathic intracranial hypertension
e. hydrocephalus
f. sleep apnea
g.cardiac cephalgia
h.acute glaucoma
Simple Treatment of Headache
-------------------------------------
Consume a painkiller.
Lie down in a dark, quiet room.
Use muscle relaxation techniques or a gentle massage.
For tension headaches, try a warm bath.
For migraines, put an ice bag or cold towel on your temple.
If the headache do not improve, go for a complete investigation of the headache.
What are the investigations done in Headache?
-------------------------------------------------------
You should be investigated for your headache if the headache has:
1. associated fever and and change in mental state.
2. numbness of part of the body or with paralysis.
3. associated fits.
4. sudden onset of severe headache
5. lasted for more than a day even after taking painkillers.
6. increased headache frequency.
7. appeared different from your usual type
8. been precipitated by coughing,sneezing,bending
9. associated with stiff neck and vomiting
10.appeared for the first time in middle age
Common tests:
Blood tests - for infections,raised ESR, bleeding disease
MRI of brain- to exclude brain tumours, bleeding in the brain
Lumbar puncture - used only if there is suspected infection of brain or meninges
Wednesday, October 10, 2007
A Simple Guide to Endometriosis
A Simple Guide to Endometriosis
---------------------------------------
What is Endometriosis ?
----------------------------
Endometriosis is a disorder of the endometrial tissues (which line a woman's uterus) in which these tissues are implanted in places outside the uterus, usually in other parts of the pelvic cavity and abdomen.
However, in women with Endometriosis, blood from the implanted endometrial tissue is trapped inside, becomes inflamed, and develops into scar tissue.
Because of this inflammation, severe pain, infertility and bowel problems occur.
What are the Causes of Endometriosis?
----------------------------------------------
The cause of endometriosis is still not known.
There are a few theories:
1.during menstruation, some of the menstrual tissue is pushed back through the fallopian tubes into the abdomen where it implants and grows.
2.it may be due to a genetic process
3.certain families are predisposed to endometriosis:
Higher socioeconomic groups
women who marry late and have no or few children
4.Stress may constrict the opening of the uterus .
Some endometrial tissues are pushed backward into the abdominal cavity instead of through the opening of the uterus
What are the Symptoms of Endometriosis?
--------------------------------------------------
Endometriosis occurs usually years after the periods begin.
Symptoms may worsen as the endometrial area increases in size.
However after menopause, the implanted tissue shrinks away and the symptoms subside.
Common symptoms include:
Severe menstrual cramps
Pelvic pain apart from menstrual periods
Diarrhoea or painful bowel movements during menses
Menstrual irreuglarities
Menorrhagia
Painful intercourse
Backache
Pain with exercise
Painful pelvic exams
Painful and frequent urination
Bloating
Constipation
Fatigue
How do you made the Diagnosis of Endometriosis ?
------------------------------------------------------------
A diagnosis can only be made via laparoscopy.
A laparoscope is a tube with a light in it which is inserted through a small incision in the navel area. The misplaced endometrial tissue can then be found and the location, extent and size of the endometriosis detected.
What is the Treatment for Endometriosis?
----------------------------------------------------------
There is no cure for endometriosis.
If the symptoms are mild, only medication for pain is required.
Treatment depends on the size, extent of the lesions, age of the patient and the desire for pregnancy.
If these women want to be pregnant, the best course of action is to have a trial period of unprotected intercourse for 6 months to 1 year.
Once pregnancy occur, the endometriosis will cleared by itself because there is no menses for nine months. Whether the endometriosis will recur after delivery depends on the patient. Most patients do not have a recurrence.
If the patient is not seeking pregnancy and where specific treatment of the endometriosis is required, hormone suppression treatment may be tried. This prevents ovulation and less endometrial tissue is formed. Because of this the endometriosis may reduced resulting in less symptoms. A course of treatment may last 6 months.
Where hormone suppression therapy do not work, some patients may require surgical treatment to remove the endometriosis tissue in the abdomen.
In severe cases, where the uterus and ovaries are affected, removal by surgery of the uterus and/or ovaries is required especially in those nearing menopause or who do not wish to be pregnant.
Monday, October 8, 2007
A Simple guide to Stress
----------------------------
What is Stress?
-----------------
Stress is a very common condition characterised by exaggerated worry and tension.
People with stress worry excessively about money, health, family, or work, even though there are no signs of trouble.
They are unable to relax and may suffer from insomnia.
What are the common warning signs of stress?
------------------------------------------------------
The signs vary from person to person.
Some of them are:
1. Headaches
2. fast heartbeats
3. Muscle tension; muscle aches
4. muscle tremors
5. Inability to concentrate
6. Stomach ache
7. Diarrhoea
8. Chest pain
9. Breathlessness; hyperventilation
10.Dry mouth
11.Excessive sweating
12.Cold clammy hands
13.Under eating or overeating
14.Anxiety or panic
15.Irritability
16.Hyperactivity
17.Loss of sex drive
18.Fatigue
19.Sense of impending doom
20.Difficulty in falling asleep or frequent nightmares
Other signs may include chills, thirst, dizziness, nausea, fainting, twitches, vomiting, weakness, stuttering,shaky and strained voice,high-pitch laughter and higher blood pressure.
Even for children of school-going age, there are stress.
Symptoms include:
1.Fear of being away from the family
2.Refusal to go to school
3.Fear of strangers
4.Fear of falling asleep or having recurrent nightmares
5.Unnecessary worry
What can we do to lower our stress level?
------------------------------------------------
There are some ways to manage Stress:
1.Be more organised.
Plan your time well.
Do a list of all the things you need to do.
Arrange them in order of importance.
Decide how much time you need for each job.
Keep to your plan.
2.Give yourself time to adjust from one change to another.
Spread out the changes in your life.
Don't do too many things at one time.
3.Always do your work according to your own ability and interest.
Be realistic about what you can do.
Do not ask for the impossible.
Set goals which are achievable so that you don't feel frustrated or discouraged.
4.Think before making decisions.
Get all the relevant information first.
Don't decide blindly.
Consider all the pros and cons of each choice.
Get the people who will be affected by the decision involved in the process.
5.Learn to like yourself.
Don't worry about your external appearance and other faults.
Make the best of what you have.
Accept what you cannot change.
6.AlwaysThink positively.
Prevent negative feelings from building up.
Try to find the source of these feelings.
Always deal constructively with them.
Do not blow things out of proportion.
7.Do not keep all your problems and worries to yourself.
Remember you are not alone.
Share your problems with your spouse, friend or supervisor .
They may have had experience with similar situations.
They may be able to solve your problem.
8.Always build a happy family.
Be kind and loving to your family.
They will provide you with love and support in your times of need.
Always set aside some time each day to talk, play or relax together.
Your home should be a happy place to return to after a hard day's work.
9.Have good friends.
You also need good friends to talk to and laugh with.
They will visit you, go out with you and help you in times of need.
Treat others the way you would like them to treat you.
Respect their views and be patient with their faults.
Always try to give and take.
10.A healthy body is important to overcome stress.
Keep healthy by exercising regularly, eating wisely and getting enough sleep.
Do not smoke or drink to relieve your stress.
Smoking and drinking do not solve anything.
They will cause more problems for your health.
11.Spend some time on yourself.
Do something that you really enjoy like a hobby or an exercise.
Take a short break when you feel tensed or tired.
You deserve to have a little fun sometimes.
12.Try to learn some Relaxation Techniques:
Deep breathing exercise,
meditation,
massage and
muscle relaxation techniques
can be helpful in relieving stress.
What is the Treatment of Stress?
---------------------------------------
Stress can be treated with conventional medicine, psychotherapy and alternative approaches.
A combination of conventional and alternative methods has been shown to be effective.
Conventional Medicine
Psychotherapy and psychoanalysis helps to identify the buried conflicts and worries that may be causing the stress.
Behaviour modification, on the other hand, focuses on changing patterns of behaviour to help the patient avert stress or to cope better with it.
Cognitive therapy similarly concentrates on changing ways of thinking.
One of the best forms of treatment for stress is daily exercise and a healthy lifestyle.
Medication relieves symptoms of stress and is often prescribed in conjunction with other therapies.
Alternative Medicine:
--------------------------
music therapy,
yoga,
herbs and
aromatherapy
are some ways that have helped stress sufferers to relax.
"Remember that you are not alone.
There are always people who are willing to help you.
In this life you must always give and take.
Be happy! Don't worry unnnecessarily!"
Monday, September 17, 2007
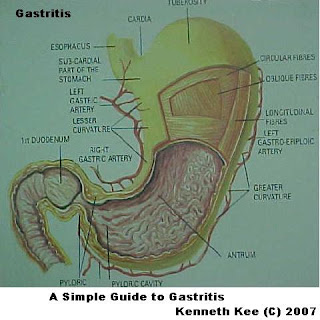
A Simple Guide to Gastritis
----------------
What is Gastritis?
-------------
It may presents as gastritis ,peptic gastric ulcer or if it extends to the duodenum(first part of small intestine) duodenal ulcers.
What are the causes of Gastritis?
--------------------------------------
Two main causes are
1.helicobacter pylori infection - this bacteria damages the protective lining of the stomach making the underlying stomach tissue more vulnerable to the acidic gastric juice.
2.excessive production of acidic gastric juice
Excessive production of acidic gastric juice burns into the protective lining of the stomach and cause inflammation of the underlying stomach tissue.
The causes of excessive production of acidic gastric juice are:
1. Most common is stress and anxiety which automatically increase the production of the acid as a result of sympathetic nervous reaction
2.hereditary- some gastric patient has family history of gastric problem. Blood group O tends to have more gastritis while Blood group A has a tendency towards stomach cancer.
3.irregular meals tend to cause more acidic gastric juice to form at regular meal time.
4.alcohol and smoking has been associated with increased acid formation
5.Drugs: prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen,
6. diseases, such as pernicious anemia, autoimmune disorders, and chronic bile reflux, can cause gastritis as well.
What are the Symptoms of Gastritis?
--------------------------------------------
The most common symptoms are
1.upper abdominal upset or pain.
Other symptoms are
2.belching, abdominal bloating,
3.nausea, and vomiting
4.indigestion or of burning in the upper abdomen or in the chest(heart burn).
5.Blood in your vomit or black stools may be a sign of bleeding in the stomach, which may indicate a serious problem requiring immediate medical attention.
How do you diagnose Gastritis?
------------------------------------
Gastritis is diagnosed through one or more medical tests:
Medical history - past and family history of gastritis
Physical examination- epigastric bloating or tenderness
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.
The doctor eases an gastroscope, a thin tube containing a tiny camera, through your mouth and down into your stomach to look at the stomach lining. The doctor will check for inflammation and may remove a tiny sample of tissue for tests(biopsy).
The biopsy will detect how bad is the inflammation or whether there are underlying cancer cells. In additional if any polyps (benign swelling of the lining of the stomach) are detected, they are removed at the same time and sent for biopsy.
Blood test. The doctor may check your blood for any evidence of H.pylori infection and your red blood cell count to see whether you have anemia, which means that you do not have enough red blood cells. Anemia can be caused by bleeding from the stomach.
Urea breath test can also determine whether you have H.pylori infection
Stool test. This test checks for the presence of blood in your stool, a sign of bleeding. Stool test may also be used to detect the presence of H. pylori in the digestive tract.
What is the Treatment of Gastritis?
------------------------------------------
The main treatment is usually
1.reduce stress
2.reorganisation of work in such a way as to be able to handle the pressure of work better as well as to have regular meals
3.Control of diet - avoid hard foods such as peanuts , tough meat, spicy food, cold food, black coffee, strong tea,citrus fruits and their juices,carbonated beverages, deep fried or oily food.
4. Take more frequent and smaller meals.
5. Avoid alcohol and smoking
6. Avoid drugs such as aspirin, painkillers,steroids which may irritate your stomach and cause increase in acid production
Medical treatment:
Treatment usually involves taking drugs
1.Antacids:to reduce stomach acid and thereby help relieve symptoms and promote healing. (Stomach acid irritates the inflamed tissue in the stomach.)
2.H2 Antagonist: to reduce to production of acidic gastric juice.(cimetidine, ranididine,omeprazole, Nexium etc)
3. Antispasmodics: anticholinergic drugs like buscopan, librax reduce the spasm in the stomach and duodenum
4. Antiflatulents - to reduce gas in the abdomen
5.If your gastritis is caused by an infection, that problem may be treated as well. For example, the doctor might prescribe antibiotics to clear up H. pylori infection.
Once the underlying problem disappears, the gastritis usually does too.
Talk to your doctor before stopping any medicine or starting any gastritis treatment on your own.
What are the Complications of untreated Gastritis?
--------------------------------------------------------------
Any untreated gastritis can cause complications such as:
1. peptic ulcers
2. bleeding ulcers
3.perforated stomach and peritonitis
Gastritis or ulcer is not healed overnight. The chances of satisfactory gastric recovery are excellent. However recurrences are always possible so do not stop your medications, good food habits and healthy lifestyle too soon.
Friday, September 14, 2007
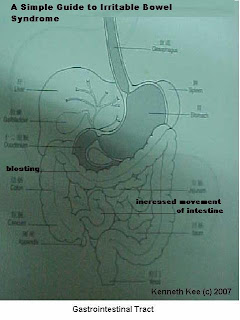
A Simple Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome
----------------------------------------------
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
------------------------------------------
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common functional disorder of the gastrointestinal system. It is characterised by abdominal pain/cramps, bloating or gas, diarrhoea and/or constipation. It is also known as spastic colon.
Who is affected by Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
--------------------------------------------
It occurs in one in five persons and usually between the ages of 20-50.
Women outnumber men by two or three to one.
It can become a chronic condition causing much discomfort and inconvenience to the patient. However, it does not progress to cancer.
What is the Cause of Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
--------------------------------------------------------
The exact cause of IBS is not known.
The muscles of the walls of the intestines in the normal person contract and relax in a co-ordinated rhythm known as peristalsis. This action helps to move food along the intestines during which time absorption takes place.
The nerves and muscles in the bowel appear to be extra sensitive in people with IBS. The contractions are stronger and last longer.
Food is pushed along the intestines at a faster rate, giving rise to abdominal pain, gas and diarrhoea. Sometimes, the opposite occurs. The contractions are weaker causing the passage of food to slow down and constipation results.
Other factors that have been shown to play a part are stress, diet and hormones. These are called triggers.
1.Stress
which may be psychological or physical.
Psychological stresses such as family misunderstanding; bereavement; anxiety; meeting deadlines etc.
Physical stresses such as illnesses, infections, exhaustion etc.
2.Diet
certain foods have been known to cause the onset of symptoms. They include fried or oily food; gas-forming foods e.g.broccoli, beans, cabbage; chocolates; coffee.
3.Hormonal changes
some women experience attacks during or around their menstrual periods.
What are the Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
----------------------------------------------------------------
The main symptoms of IBS are:
1.Abdominal pain or cramps-usually over the left side or over the lower abdomen
2.Bloating and/or gas
3.Diarrhoea, constipation or alternating diarrhoea and constipation.
4.whitish mucus in the stool
The symptoms can range from mild to severe.
In many cases the symptoms are bearable and go off after a bowel movement.
Women with IBS often have more symptoms during their menstrual periods.
How do you make the Diagnosis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Because the cause is unknown and there is a lack of specific physical signs, diagnosis is arrived at through a process of elimination .
A colonoscopy is usually done to rule out colon cancer, diverticulosis, polyps.
What is the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
--------------------------------------------------------------
There is no real cure for Irritable Bowel Syndrome.
Treatment is mainly symptomatic i.e. it is directed towards the relief of symptoms.
Mild symptoms usually go off on their own.
If symptoms are severe, the doctor may prescribe the following:
Anti-spasmodics for the abdominal pain and cramps,
Anti-flatulents to get rid of gas and relief the bloating,
Anti-diarrhoeals to stop diarrhoea,
Antidepressants, even in lower doses than are used for treating depression, can help people with IBS.
Laxatives to relief constipation.
Foods and drinks that may cause or worsen symptoms include:
fatty foods, like french fries
milk products, like cheese or ice cream
chocolate
alcohol
caffeinated drinks, like coffee
carbonated drinks, like soda
Some foods make IBS better.
Fiber may reduce the constipation associated with IBS because it makes stool soft and easier to pass.
However, some people with IBS who have more sensitive nerves may feel a bit more abdominal discomfort after adding more fiber to their diet. Fiber is found in foods such as breads, cereals, beans, fruits, and vegetables.
Too much fiber at once can cause gas, which can trigger symptoms in a person with IBS.
Eat small meals for example eating four or five small meals a day.
Large meals can cause cramping and diarrhea in people with IBS.
Stress doesn’t cause IBS, but it can make your symptoms worse.
Learning to reduce stress can help with IBS. With less stress, you may find you have less cramping and pain. You may also find it easier to manage your symptoms.
Meditation, exercise, hypnosis, and counseling may help.
What can be done to prevent Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
------------------------------------------------------------------
Prevention is an important part in the total management of this condition.
They consist of stress management and life-style changes.
Stress management
Avoid unnecessary stress
Learn to relax
Exercise regularly
Dietary changes
Avoid oily, spicy food
Avoid gas-forming foods e.g. cabbage, broccoli, beans
Avoid coffee, chocolates, and alcohol
Avoid large meals
Take more fibre
Monday, September 10, 2007
A Simple Guide to Alopecia(Hair Loss)

------------------------------------
What is Alopecia(Hair Loss)?
-----------------------------------
Alopecia or Hair Loss is the partial or complete loss of hair in the scalp, armpit or other areas of the body to the extent that skin is evident and sparse amount of hair is present or completely absent. Hair loss usually develops gradually and may be patchy or diffuse (all over)
Who get Alopecia?
-----------------------
Hair loss is experienced by both men and women, young or old.
What is the cause of Alopecia?
-------------------------------------
The hair is made up of keratin, the same protein that is found in nails and the outer layer of our skin. The average adult has more than 100,000 strands of hair on his scalp.
1.genes(Male pattern baldness, Congenital),
2.hormones(excessive DHT or dihydrotestosterone)
Women are protected from male pattern baldness because they produce less androgens, and because their female hormones, estrogen can counter the effect of their male hormones. However, women who produce excess androgens may have male pattern baldness.
5.Improper hair care
6.Burns - Excessive heat damages the cells of the skin including the hair roots.
7.Infectious diseases such as syphilis and fungal infection can cause damage to the hair roots.
-------------------------------------------------------
Male pattern baldness (or androgenetic alopecia) accounts for the majority of all hair losses. This is the most common type of baldness in men, especially older men.
Besides male pattern baldness, there are various other types of hair loss.
Temporary hair loss (telogen effluvium): Here clumps of hair begin to fall out suddenly over a few days. It can be caused by severe stress, childbirth, severe illnesses, surgery and some medications. As its name implies, its effect is usually temporary.
Compulsive hair pulling (trichotillomania): This causes hair breakage and usually leaves the scalp undamaged. It usually affects children and women and has been linked to a psychological cause.
Traction alopecia: This is hair loss caused by certain hairstyles such as ponytails, buns or braids that pull excessively on the hair.
-------------------------------------------
1.Microscopic examination of a plucked hair
What is the Treatment and Prevention of Alopecia?
--------------------------------------------------------------
It is important to determine the underlying cause before treatment.
2.Minoxidil is available over the counter. . It is applied on the scalp and works by reversing the regression of hair follicles caused by hormones.It takes a few months before any effect can be seen.
Hair loss from menopause or childbirth often returns to normal 6 months to 2 years later.
For hair loss due to heredity, age, and hormones, the topical medication minoxidil can be helpful for both male and female pattern baldness. You may need to wait 6 months before you see results.
Hair transplants performed by a physician is a surgical approach to transferring growing hair from one part of the head to another. It is somewhat painful and expensive, but usually permanent.
Tuesday, August 28, 2007
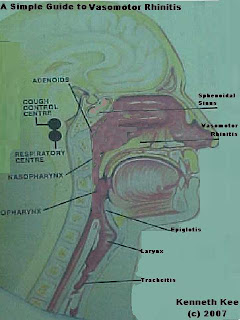
A Simple Guide to Vasomotor rhinitis
--------------------------------------
What is Vasomotor Rhinitis?
-----------------------------
Vasomotor Rhinitis is a condition which consists of a group of symptoms that include a runny nose, itchiness and sneezing, that are caused by irritation and congestion in the nose. It is brought about by changes in vascular tone and permeability.
What are the symptoms of Vasomotor rhinitis?
--------------------------------------------------
The symptoms of Vasomotor rhinitis include:
Recurring nasal inflammation
Sneezing
Runny nose
Profuse watery nasal discharge
Nasal membrane swelling
What causes Vasomotor rhinitis?
---------------------------------------
Vasomotor rhinitis occurs as a result of a response of the nasal membrane to
1.irritants such as smoke,
2.temperature changes and
3.stress.
Other causes of chronic rhinitis are blockage in the nose e.g. nasal polyps, enlarged adenoids and a deviated septum that impede mucus drainage and restrict air flow. Medications can cause rhinitis or worsen it in people with allergies, vasomotor rhinitis or a deviated septum.
Prolonged use of nasal decongestants can worsen rhinitis.
Some blood pressure medications such as beta blockers and vasodilators can cause rhinitis.
What is the difference between Allergic rhinitis and Vasomotor Rhinitis?
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Allergic rhinitis could be seasonal or perennial (year round).
Seasonal rhinitis is due to pollen or mould spores.
Perennial rhinitis are due to allergens such as house dust mites, animal dander or moulds found on carpets or furniture upholstery and even some foods.
Non-allergic rhinitis can also be triggered by cigarette smoke and many other air pollutants, strong odours, exposure to cold and alcohol. Smoking and air pollution may also cause symptoms by damaging the cilia (hair cells) which moves mucus through the air passages.
Hormonal changes in pregnancy cause "Rhinitis in Pregnancy". The expecting mother will recover once the baby is delivered.
What treatments are available for Vasomotor rhinitis?
----------------------------------------------------------------
Treatments for Vasomotor rhinitis include:
Non-medical:
----------------
Avoid dry air
Keeping air moist
Vapourisers
Nasal Decongestant sprays are not recommended for treatment of vasomotor rhinitis
Complete avoidance of environmental allergens may be impossible but it can be minimised for example removing carpets and pets.
Use a pollen mask when mowing the grass or cleaning the house
Install an air purifier
Change the air filters monthly in heating and air conditioning systems
use cotton or synthetic materials such as Dacron in pillows and bedding
enclose mattress in plastic
keep windows closed during high pollen times
eliminate house plants
bathe pets frequently or even give away dander–producing pets.
Avoid Nasal irritants which can cause typical immune response seen with classical allergies. Examples include cigarette smoke, perfume, aerosol sprays, smoke, and smog and car exhaust
Nasal irrigation utilizing a buffered hyper tonic saline solution helps to reduce swollen and congested nasal and sinus tissues.
It also washes out thickened nasal secretions, irritants (smog, pollens, etc.), bacteria, and crusts from the nose and sinuses.
While irrigating the nose, it is best to stand over the sink and irrigate each side of your nose.
Aim the stream toward the back of your head, not at the top of your head.
For young children, the salt water can be put into a small spray container which can be squirted many times into each side of the nose.
Medical:
---------
Anti-histamines provide good relief for mild to moderate symptoms.
Newer antihistamines that are long-acting and less likely to cause drowsiness have been found to be useful.
Decongestants such as pseudoephedrine can help to shrink the swollen tissues caused by irritants and other causes. However decongestant nasal sprays are not advised because they cause a a rebound effect on nasal tissues(initially the nasal tissue shrinks but later they become more swollen)
Corticosteroids in the form of nasal spray reduce the immune response and may be prescribed to reduce severe symptoms.
These drugs are highly effective in allergic patients; but there is a potential for serious side effects when used over time. They are best used for the short term management of allergic problems, and their use must always be monitored by a physician.
Nasalcrom (cromolyn sodium): This spray helps to stabilize allergy cells (mast cells) by preventing release of allergy mediators, like histamine.
Immunotherapy:Allergy shots interfere with the allergic response. After identification of an allergen, small amounts of it are given back to the sensitive patient. Over time the patient will develop blocking antibodies to the allergen, and they become less sensitive and less reactive to the substance causing allergic symptoms. This is the best treatment provided the allergen is correctly identified.
Surgery:Nasal polyps, enlarged adenoids and deviated septums can be corrected with surgery. Obviously this should be done only after more conservative measures have been tried. Surgery is not a replacement for good allergy control and treatment.
Friday, August 17, 2007
A Simple Guide to Shingles

-----------------------------
What is Shingles?
--------------------
Shingles or Herpes zoster is a condition where a crop of blisters caused by the varicella zoster virus form a band across one side of the chest, abdomen or face.
What is the cause of shingles?
----------------------------------
The same virus that causes chicken pox causes shingles.
The chickenpox virus remains in a dormant state in certain nerve cells of the body from months to many years, and then reactivates, causing shingles.
This infection is due to a temporary decrease in the body's resistance, allowing the virus to start multiplying and to move along nerve fibres towards the skin.
Who are the People at risk of getting Shingles?
-------------------------------------------------------
About 1 in 10 people who had chickenpox as children will develop shingles as adults.
The disease occurs
1.more often in older people (over 50 years old) because the immune response is believed to be weaker in older people.
2.Trauma or possibly stress may also contribute to an attack of shingles.
3.Weakened Immune system people like those with cancer, eg. Leukaemia, lymphoma, undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer, patients with organ transplants and taking drugs to ward off transplant rejection and patients with diseases that lowers the immune system eg. AIDS.
What are the symptoms of shingles?
-------------------------------------------
The first symptom is a burning pain or tingling and extreme sensitivity in one area of the skin.
This may be present for one to three days before a red rash occurs.
A group of blisters then forms on a red base which looks like chicken pox lesions.
The blisters generally last for two to three weeks, during which time they accumulate pus and then crust over and begin to disappear.
The pain may last longer for a month or longer.
A slight discoloration or scarring of the skin is also possible.
How severe is the pain of Shingles?
-----------------------------------------
The pain is usually severe enough for the doctor to prescribe painkillers.
A long-lasting painful complication of shingles called post-herpetic neuralgia occurs in some older patients.
This may last long after the shingles have healed.
For these people the slightest touch or contact with clothing can be unbearable.
Where do shingles appear on the body?
----------------------------------------------
Shingles generally affect only one side of the body.
Most commonly, blisters will appear on the chest or abdomen, including the buttocks and genitalia, and even the face.
If the blisters involve the eye region, permanent eye damage can result.
Your doctor will refer you immediately to an eye specialist when such a complication develops.
What are the complications of Shingles?
------------------------------------------------
Post-herpetic neuralgia, a condition in which either constant or episodic pain persists for a long time after the skin has healed.
About 50% of affected patients are over the age of 60 years.
The chronic pain is believed to be due the damage to nerve endings.
People who suffer this long-term pain may experience psychological suffering such as depression, insomnia and weight loss.
Infection of the blisters by bacteria can also cause delayed healing of the skin.
Antibiotic treatment is needed.
If the shingles affects the forehead, sometimes inflammation of ophthalmic nerve of the eye may occur. It may cause severe pain in the eye and cause blindness. Damage to the cornea may also occur.
If the shingles affect the the ear, it may cause pain, tinnitus (buzzing sound in the ear), dizziness, loss of hearing or an increased risk of spread to the brain.
In patients with weakened immune systems, there may be high fever and spread of the disease all over the body.
Is shingles contagious?
---------------------------
Shingles is much less contagious than chicken pox.
People with shingles can spread the virus if blisters are broken to someone who has never had chicken pox or who is already ill.
The people who are at risk include babies and those who already are ill such as cancer patients.
These people will develop chickenpox.
How severe is the pain of Shingles?
----------------------------------------
The pain is usually severe enough for the doctor to prescribe painkillers.
A long-lasting painful complication of shingles called post-herpetic neuralgia occurs in some older patients. This may last long after the shingles have healed.
For these people the slightest touch or contact with clothing can be unbearable.
Does Shingles cause much scarring?
-----------------------------------
Shingles can result in scarring if the blisters are infected or if the patients have used toxic home remedies on the blisters.
Some Chinese physicians believe that a snake in the skin causes the disease and the head of the snake must be burned with chemicals in order to stop the snake from growing.
How is shingles treated?
-----------------------------
In most cases Shingles clears on its own in a few weeks and seldom recurs.
Treatment consists of painkillers, as well as cool compresses to help dry the blisters.
Antibiotics are given if there is bacterial infection.
The antiviral drug, acyclovir, may be given especially for patients with eye involvement or who are very ill.
It is useful only if it is started early in the disease.
The earlier it is taken after the disease begins the better the effect.
The drug might prevent post-herpetic neuralgia.
Post-herpetic neuralgia can be treated with painkillers and high doses of tranquilisers at night.
Wednesday, August 8, 2007
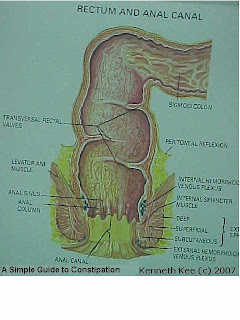
A Simple Guide to Constipation
--------------------------
Constipation by definition is a condition which is characterised by fewer than normal bowel movement than usual.
It is accompanied by straining, incomplete evacuation and passage of hard stools.
Who gets Constipation?
----------------------------
It is particularly common among the elderly and younger children.
How do you get Constipation?
-----------------------------------
There are a few causes of constipation:
1. Insufficient fibre(fruits,vegetables) to form bulk in the stools.
2. Insufficient fluid in the diet(at least 8 glasses of water).
3. Insufficient time to go to toilet when there is the urge to pass motion.
4. Insufficient exercise to help the intestine to move especially after meals, common in
sedentary jobs and older people
5. Stress cause the constriction of the anal sphincter preventing the stools from passing.
6. Depression on the other hand depress the movement of the intestines.
7. Drugs like cough mixture containing codeine,antispasmodic, antacids may also reduce the
motility of the intestine.
8. Pregnancy in the later stage cause the womb to press against the intestine.
9. People with low thyroid hormone slows down the movement of the intestines.
10.People with piles or pelvic space occupying swelling which may press against the
intestine or rectum.
How to avoid Constipation?
--------------------------------
Avoidance of constipation include:
1. Increase in daily fibre intake to at least 15gm (eg. 1 bowl of bran cereal for breakfast),
fruits and vegetables).
Fibre increases the bulk of the stool allowing easy passage of stools through the large
intestine.
2. Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day (2 litres). Water reduces the hardness of stools.
3. Regular exercises at least 2-3 times a day especially after meals. Exercise will enhance
intestinal movement.
4. Allow a distraction free period of 15 min a day for bowel movement. The strongest
intestinal movement occurs after breakfast.
5. Do not ignore or suppress the urge to pass bowel movement. This may impair the
sensation to detect initiation of bowel movement leading to constipation.
How to treat Constipation?
--------------------------------
1.Follow the advice above.
2.Consult your family doctor to exclude any abdominal swelling which may be blocking the
passage of stools.
A colonoscopy may be needed to check the large intestines for tumours or early cancer.
Your piles may be removed during the colonoscopy if found to be obstructing passage of
stools.
3.Try Yogurt or fermented milk with lactobacillus as a method to stimulate more
production of bulk in stools.
4.Try not to take laxatives unless it is deemed necessary by your doctor.
Most doctors preferred not to use medicine in combating constipation.
5. Learn to relax the anal sphincter by doing some pelvic exercises
Subscribe Now: Feed Icon
Clicktale
Labels
- abdominal pain (10)
- abnormal brain signals (1)
- abscess (1)
- Achilles tendinitis (1)
- acid reflux (2)
- acne (1)
- Acne Rosacea (1)
- Acoustic neuroma (1)
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (1)
- acyclovir (2)
- ADDISON DISEASE (1)
- Adenoidectomy (1)
- Adenoiditis (1)
- Adenoids (1)
- Aedes mosquitoes (2)
- aerobics (1)
- aging (2)
- AIDS (2)
- air conditioners (1)
- alcohol (5)
- Alcoholism (1)
- allergens (2)
- allergies (1)
- allergy (2)
- alopecia (1)
- alzeheimer's disease (1)
- amblyopia (2)
- amebiasis (1)
- Amenorrhea (1)
- amylotrophic lateral sclerosis (1)
- anaemia (4)
- anaerobic bacteria (2)
- Anal fissure (1)
- Anal Fistula (1)
- analgesic (4)
- androgens (1)
- ANDROPAUSE (1)
- anger management (1)
- Angiogram (1)
- ankles (1)
- anopheles mosquito (1)
- anorectal abscess (1)
- anovulation (1)
- Answers (3)
- Anthrax (1)
- anti-aging (1)
- anti-diarrhoea (1)
- anti-flatulent (1)
- antibiotic (8)
- Antibiotic therapy (1)
- antibiotics (26)
- anticholinesterase (1)
- anticoagulant (1)
- antidepressant (1)
- antifungal (3)
- antihistamine (4)
- antimycotics (1)
- antioxidants (1)
- antispasmodic (2)
- Antispasmodics (1)
- antitoxins (1)
- antiviral (1)
- anus (2)
- anxiety (2)
- aphthous ulcers (1)
- Appendicitis (1)
- appendix perforation (1)
- appetite suppressant (1)
- areflexia (1)
- artane (1)
- Artery blockage (1)
- arthritis (4)
- articular cartilage injury (1)
- asbestos (1)
- aspiration (2)
- aspirin (1)
- asthma (1)
- Astigmatism (1)
- atherosclerosis (1)
- Athlete's Foot (1)
- atopic dermatitis (1)
- atopic eczema (2)
- atrial fibrillation (2)
- atrophic vaginitis (1)
- aural toilet (1)
- autoimmune disease (3)
- autoimmune neuromuscular disease (1)
- autonomic dysfunction (1)
- avitaminosis (1)
- avoid causative substance (1)
- avoid prolonged standing ulcers (1)
- avoid rubbing (1)
- avoid straining (1)
- avoid sudden movement (1)
- avoid touching the acne (1)
- axilla (1)
- back pain (1)
- Backache (2)
- Baclofen (1)
- bacteria (15)
- bacteria culture (4)
- bacterial (4)
- bacterial infection (6)
- bacterial vaginosis (1)
- bad posture (1)
- baking soda (1)
- Balanitis (1)
- ballooning (1)
- ballooning of blood vessel in brain (1)
- barking cough (1)
- bartholin cyst (1)
- basal cell carcinoma (1)
- Basal ganglia (1)
- bed bugs (1)
- bed sores (1)
- Bedding and clothing (1)
- bedwetting (2)
- bees (1)
- Beestings (1)
- Bence Jones (1)
- benign (3)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (1)
- Benzyl Benzoate lotion (1)
- Besy ahoo answer (1)
- beta blockers (1)
- biological targeted therapy. (1)
- biological warfare (1)
- biopsy (4)
- bipolar disorders (1)
- bipolar disorders treatment (1)
- bird flu (1)
- birth control (1)
- birth control methods (1)
- bladder cancer (3)
- bleeding (6)
- bleeding disorder (2)
- bleeding ulcers (1)
- Blepharitis (1)
- blindnes (1)
- blindness (4)
- blisters (3)
- bloating (5)
- blocked nose or ear (1)
- blocked opening of glands (1)
- Blood blockage (2)
- blood cancer (2)
- blood in sputum (1)
- blood in urine (2)
- blood loss (1)
- blood pressure (1)
- blood release (1)
- blood transfusion (2)
- bloodborne infection (1)
- blurred vision (4)
- BMI (1)
- bodyache (2)
- bone density test (1)
- bone fusion (1)
- bone infection (1)
- bone marrow transplant (3)
- bone pain (1)
- Bordetella pertussis (1)
- bowel movement (1)
- BPH (1)
- brace (1)
- bradyacardia (1)
- brain damge (1)
- brain infections (2)
- brain tumour (2)
- breast (1)
- breast cancer (1)
- breathless (6)
- brittle bones (1)
- broken blood vessels (1)
- Bronchitis (1)
- bronchodilator (2)
- bronchoscopy (1)
- bruise (1)
- BSE (1)
- Buerger's Disease (1)
- bulbar (1)
- burn calories (3)
- burning sensation (1)
- Burns (1)
- burrow lines on the skin (1)
- buttocks (1)
- CA 125 (1)
- calcium (1)
- calcium supplements (1)
- cancer (9)
- cancer of the cervix (1)
- cancer of vulva (1)
- Cancer screening (5)
- cancers (1)
- Candida albicans (2)
- Candidiasis (1)
- Carbamazepine (1)
- carbohydrate diet (1)
- cardiac tamponade (1)
- cardiogenic shock (1)
- cardiovascular collapse (1)
- cardioversion (2)
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (1)
- CAT Scan (1)
- cataract (1)
- Caudate nucleus (1)
- cautery (1)
- CD4 (T-cell) lymphocytes (1)
- Cellulitis (1)
- Central nervous system (1)
- cerebral aneurysm (1)
- cerebral palsy (1)
- cerebrovascular accident(CVA) (1)
- cervical cancer (2)
- Cervical Spondylosis (1)
- cervicitis (2)
- cervix cancer (1)
- cessation of menstruation (1)
- chalazion (1)
- changes in personality and behaviour (1)
- chemical treatment (1)
- chemicals (7)
- chemotherapy (10)
- chickenpox (2)
- chikungunya fever (1)
- child school problems (1)
- childhood (1)
- chills (1)
- Chlamydia (1)
- Cholecystectomy (1)
- Cholecystitis (2)
- Cholera (1)
- cholesterol (2)
- Choreia (disease) (1)
- choroid (2)
- chronic (4)
- chronic bronchitis (1)
- chronic fatigue (1)
- chronic illness (2)
- Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (2)
- chronic pelvic pain. endometrosis (1)
- chronic suppurative otitis media (1)
- Cialis (1)
- cigarettes (1)
- ciliary body (1)
- ciprofloxacin (1)
- circumcision (1)
- cirrhosis.cold compress (2)
- cleaning (1)
- clofazimine (1)
- closed angle glaucoma (1)
- clusters (2)
- coccyx injury (1)
- cochlea (1)
- Coeliac Disease (1)
- cold compress (3)
- cold sores (1)
- cold temperatures (1)
- colic (1)
- collagen abnormalities (1)
- colon (1)
- colon cancer (1)
- colonoscopy (1)
- common (1)
- common cold (1)
- compression (2)
- compression of the median nerve (1)
- Conditions and Diseases (2)
- condoms (1)
- congenital (3)
- congenital deformities (1)
- congestion (1)
- congestive heart failure (1)
- conjuctivitis (2)
- conjuntiva (1)
- constipation (5)
- contact dermatitis (1)
- contact lens (4)
- contagious (1)
- contaminated food (2)
- contaminated soil (1)
- contaminated water and food (1)
- contents (1)
- contraction of the diaphragm (1)
- control diet (2)
- contusion (1)
- convulsions (1)
- cornea (1)
- corneal blockage (1)
- corneal ulcer (2)
- coronary artery bypass graft surgery (1)
- Coronary Heart Disease (1)
- corticosteroid creams (2)
- corticosteroid injections. (1)
- corticosteroids (3)
- cortisone injections (1)
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae (1)
- cough (7)
- CPAP (1)
- cramps (1)
- Crohn's Disease (1)
- crooked spine (1)
- Croup (1)
- CSF (1)
- curvature (1)
- CUSHING SYNDROME (1)
- cut (1)
- Cutaneous (1)
- Cutaneous Larva migrans (1)
- cystine (1)
- cystitis (1)
- cystoscopy (2)
- Cytomegalovirus (1)
- Dandruff (1)
- danger in pregnant mothers (1)
- danger of kidney and heart problems (2)
- dapsone (1)
- De Quarvian's Disease (1)
- deafness (3)
- decongestant (1)
- deep vein thrombosis (2)
- deformities (1)
- degree (1)
- dehydration (3)
- dementia (2)
- Demyelinating Diseases (1)
- dengue (1)
- Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever (1)
- Dengue Shock Syndrome (1)
- dental caries (1)
- dental hygiene (1)
- dental pain (1)
- Dental problems (1)
- depression (5)
- dermatophytes (1)
- desensitisation (1)
- diabetes (7)
- diabetes insipus (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus (2)
- dialysis (1)
- dialysis or transplant (1)
- diarrhea (6)
- diarrhoea (1)
- diastolic (1)
- diet (5)
- difficult breathing (1)
- diphenhydramine (1)
- Diphtheria (1)
- disability (1)
- discharge (1)
- discharge fom penis or vagina (1)
- dislocation of elbow (1)
- dislocation of shoulder (1)
- disorientation (1)
- diuretic (1)
- Diverticulitis (1)
- Diverticulosis (1)
- dizziness (1)
- dopamine transmitter (1)
- Down's Syndrome (2)
- drainage of pus (1)
- dribbling (2)
- drink more water (1)
- drug addict counselling (1)
- drug addicts (1)
- drugs (4)
- dry (3)
- drying agents (1)
- dryness (1)
- DTP vaccine (2)
- Duchenne (1)
- duchenne muscle dystrophy (1)
- DUPUYTREN'S CONTRACTURE (1)
- dust (3)
- dust mites (1)
- dysentery (2)
- Dysmenorrhea (1)
- dyspepsia (1)
- dysphagia (2)
- ear canal polyp (1)
- ear infections (1)
- ear pain (1)
- ear tugging (1)
- earache (1)
- earlobe infection (1)
- early 20 (1)
- eating disorders (1)
- ecchymosis (1)
- ECG (1)
- ectopic pregnancy (1)
- ECU tendonitis (1)
- Eczema (1)
- edema (1)
- elastic stockings (1)
- electricity (1)
- electrocardiogram (1)
- emergency (5)
- EMG (1)
- emotional (1)
- emphysema (1)
- encephalitis (3)
- endometrial tissues (1)
- Endometriosis (2)
- enlarged liver (1)
- enlarged liver and spleen (1)
- enlarged lymph nodes (2)
- enlarged neck nodes (1)
- enlarged tonsils (2)
- enlarged uterus (1)
- entecavir (1)
- enteric virus (1)
- Entropion (1)
- enuresis (2)
- Epididymitis (1)
- epiglottis flip backwards (1)
- epilepsy (1)
- epistaxis (1)
- Epstein-Barr virus (3)
- Erectile dysfunction (1)
- erosions (1)
- erythrodermic (1)
- erythromycin (1)
- essential (1)
- eustachian tubes (1)
- excess thyroid hormones (1)
- Excessive Menstrual Bleeding (1)
- excessive use of voice (1)
- excessive vaginal bleeding (1)
- exercise (8)
- extent (1)
- eye (1)
- eye injuries (1)
- eye ointment (1)
- eye pain (1)
- eye protection (1)
- eye strain (1)
- eyedrops (2)
- eyelashes (1)
- eyepads (1)
- eyes (1)
- facial massage (1)
- facial palsy (1)
- family history (2)
- Family Medical Doctor (40)
- fast growing (1)
- fast heart beat (1)
- fast heartbeats (1)
- fat absorption suppressant (1)
- fatigue (2)
- fear (1)
- female hormones (1)
- female predominance (1)
- fever (22)
- fiber (1)
- fibrates (1)
- fibre (1)
- fibroid (1)
- fibroids (1)
- Fibromyalgia (2)
- fibrosis (1)
- fibrous tissue (2)
- filiform (1)
- Finasteride (1)
- finger nails (1)
- fish skin (1)
- fits (1)
- flat foot (1)
- fluid (1)
- fluids (3)
- foetal development (1)
- folic acid (1)
- folic acid deficiciency (1)
- Folliculitis (2)
- food allergy (1)
- food triggers (1)
- Foot and Mouth Disease (1)
- Foot care (2)
- footwear (1)
- foreign bodies (2)
- forgetfulness (1)
- fracture (1)
- fractures (2)
- frequency (4)
- frequent cystitis (1)
- frequent urine (1)
- Frozen Shoulder (1)
- full stomach (1)
- functional (1)
- functional disorder (1)
- fungal (4)
- fungi infection (1)
- fungus (1)
- fungus Malassezia furfur (1)
- fusion (1)
- g6pd deficiency (1)
- Gait abnormality (1)
- gallbladder (1)
- gallbldder (1)
- gallstone (1)
- gallstones (1)
- ganglion (1)
- ganglion cyst (1)
- gangrene (2)
- gas (1)
- gastritis (2)
- gastroscopy (2)
- generalised rash (4)
- genes (2)
- genetic (8)
- genetic factor (2)
- genetics (1)
- Genital Herpes (1)
- genital warts (1)
- gerd treatment (2)
- german measles (1)
- Gestational diabetes (1)
- giant cell arteritis (1)
- giardiasis (2)
- giddiness (1)
- giddy (1)
- Gingivitis (1)
- glans (1)
- glass (1)
- glaucoma (1)
- Glomerulonephritis (1)
- Glossitis (1)
- Gluten Enteropathy (1)
- goiter (1)
- good dental hygiene (1)
- good posture (1)
- gout (1)
- gradual onset (1)
- gram negative bacteria (1)
- gram positive (1)
- grand mal (1)
- grayish tonsillar exudate (1)
- groins (1)
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome (1)
- gum boils (1)
- guttate (1)
- gynecologic cancer (1)
- gynecological cancer (1)
- Gynecomastia (1)
- hair follicles (1)
- hair loss (1)
- hair transplant (1)
- hair weaving (1)
- Halitosis (1)
- hallux vulgus (1)
- halos (1)
- Hand (1)
- hand hygiene (1)
- hard large stools (1)
- harden stools (1)
- hasty swallowing of food or air (1)
- HBV virus infection (1)
- HCV (1)
- HCV antibodies (1)
- HDL (1)
- head injury (2)
- headache (10)
- Health (1)
- Health education (2)
- health issues (1)
- healthy life stye (1)
- healthy lifestyle (6)
- hearing loss (1)
- heart (1)
- heart attack (1)
- heart disease (1)
- heartburn (2)
- heat (1)
- Heat Stroke (1)
- heel pads (1)
- Helicobacter pylori (2)
- heliobactor pylori (1)
- helpless (1)
- hemophilia (1)
- hemorrhage (1)
- HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA (2)
- Hepatitis (1)
- Hepatitis A (1)
- hepatitis A virus(HAV) (1)
- hepatitis B (2)
- Hepatitis C (1)
- hepatitis virus (1)
- hepatitis. (2)
- hepatocytes (1)
- herald patch (1)
- hereditary (7)
- herniorrhaphy (1)
- herpes virus (1)
- herpes zoster (1)
- hiatus hernia (1)
- hiccup (1)
- high blood pressure (1)
- high cholesterod (1)
- high cholesterol (1)
- high level (1)
- high mortality (2)
- high protein food (1)
- hips (1)
- histamine (1)
- HIV (2)
- HMB-45-positive (1)
- HMF (1)
- holes (1)
- hormonal (2)
- hormonal imbalance (1)
- hormone (3)
- Hormone replacement therapy (1)
- hormone treatment (1)
- hornets (1)
- hot flushes (1)
- HPV (1)
- HPV DNA test (1)
- HRT (1)
- HSV1 (1)
- HSV2 viruses (1)
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (1)
- Human papilloma virus Infection (1)
- human papillomavirus (2)
- Huntington (1)
- Huntington's disease (1)
- Hydrocoele (1)
- hypercalcemia (1)
- hyperextended knees (1)
- Hyperhidrosis (1)
- HYPERKALEMIA (1)
- hypernatremia (1)
- hyperparathyroidism (1)
- Hypertension (4)
- Hyperthyroid Disease (1)
- hypnotherapy (1)
- hypocalcemia (1)
- hypokalemia (1)
- hyponatremia (1)
- hypoparathyroidism (1)
- hypothyroid (1)
- hypothyroidism (1)
- hysterectomy (1)
- i/v fluids (1)
- Ichthyosis (1)
- IgM antibodies (1)
- immature blood cells (1)
- immunosuppressant (1)
- immunotherapy (2)
- Impetigo (1)
- incised and drained (1)
- index by labels (1)
- infected crust (2)
- infected oil gland (2)
- infection (4)
- infection. hair follicle (1)
- infections (7)
- infectious (3)
- Infectious Mononucleosis (1)
- infertility (3)
- infertility. (1)
- inflammation (7)
- inflammation of airway (1)
- inflammation of the mouth (1)
- influeza (3)
- infranuclear (1)
- Inguinal hernia (1)
- inhalation (1)
- inherited (1)
- inherited blood clotting (1)
- injection (1)
- injuries (1)
- injury (8)
- insects (1)
- insomnia (1)
- insufficient blood flow (1)
- insufficient haemaglobin (1)
- insulin (2)
- interferon (1)
- intermittent claudication (1)
- Intertrigo (1)
- intestinal (2)
- intestinal perforation (1)
- intestines (1)
- intraocular pressure (1)
- intrauterine device (1)
- intussusception (1)
- invasive (2)
- inverse (1)
- iris (1)
- iron (1)
- irregular meals (1)
- irregular menses (1)
- irregular rhythm (1)
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (1)
- irritants (1)
- irritation (1)
- isorbide (1)
- itch (6)
- Itchiness (1)
- itching (2)
- itchy (2)
- itchy nose (1)
- IUD (1)
- jaundice (5)
- joint pain (1)
- joints (2)
- KAWASAKI DISEASE (1)
- keloid (1)
- kidney (2)
- Kidney cancer (1)
- kidney damage (1)
- kidney disease (3)
- Klinefelter's Syndrome (1)
- Knee cap dislocation (1)
- knee ligaments injury (1)
- knee Xray (1)
- knees (1)
- knock (1)
- Koplik's spots (1)
- laceration (1)
- lactobacillus bacteria (1)
- laminectomy (1)
- lamivudine (1)
- laparoscope (1)
- lapband (1)
- Laryngeal cancer (1)
- Laryngitis (1)
- laryngopharyngeal reflux (1)
- Laryngx (1)
- laser (1)
- laser coagulation (1)
- laser surgery (1)
- LASIK (1)
- LASIK surgery (1)
- late teen (1)
- latent (1)
- LDL (1)
- leg (1)
- Legionnaire's Disease (1)
- lens transplant (1)
- leprosy (1)
- leptospirosis (2)
- leucocytosis (1)
- leukemia (1)
- levadopa (1)
- Levitra (1)
- Lice (1)
- lichen planus (1)
- life threatening (1)
- lifelong (2)
- ligamentous sheath (1)
- light sensitivity (1)
- limping (1)
- lipids (1)
- lipoma (1)
- liposarcoma (1)
- liposuction (1)
- Little's area (1)
- liver (1)
- liver cancer (3)
- Liver Cirrhosis (2)
- liver dysfunction. (1)
- Longo technique (1)
- loose ligaments (1)
- lose weight (3)
- loss in life events (1)
- loss of appetite (3)
- loss of memory (1)
- loss of mobilty (1)
- lots of water (1)
- low calcium (1)
- low fibre (1)
- low level (1)
- low oestrogens (2)
- low platelets (1)
- low thyroid (1)
- low Vitamin D (1)
- lower abdominal cramp (1)
- lower abdominal pain (1)
- lower immunity (1)
- lumbar spinal stenosis (1)
- lump (1)
- lump in neck (1)
- lung cancer (2)
- lymph node enlargement (1)
- lymph nodes (2)
- lymphatic system (1)
- lymphocytes (1)
- lymphoma (2)
- M proteins (1)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (1)
- maic attacks (1)
- major cosmetic surgery (1)
- malaria (1)
- Malathion 0.5% lotion (1)
- male baldness (1)
- MALE MENOPAUSE (1)
- malignant (3)
- mammogram (1)
- mandibular branches (1)
- marfan's syndrome (1)
- massage therapy (1)
- mast cells stimulant (1)
- Mastitis (1)
- maxillary (1)
- McBurney's Point (1)
- measles (2)
- Medical case Studies (125)
- medical conditions (5)
- medication side effects (2)
- medications (3)
- medicine (1)
- medicines (2)
- meditation (2)
- megacolon (1)
- melanin (1)
- melanoma (1)
- memory loss (1)
- men (1)
- Meniere's Disease (1)
- meningitis (2)
- meningococcus (1)
- meniscus tears (1)
- menopause (3)
- menorrhagia (3)
- mental illness (1)
- mental retardation (1)
- metal (1)
- methotrexate (1)
- metronidazole (1)
- migraine (1)
- mild fever (1)
- mildly contagious (1)
- minoxidil (1)
- miscarriage (1)
- MMR vaccine (3)
- moist (1)
- moisturizer (1)
- MOLLUSUM CONTAGIOSUM (1)
- mood changes (1)
- mood swings (1)
- motivation (1)
- motor disabilities (1)
- motor neurone disease (1)
- mouth (1)
- mouth ulcers (3)
- mouth washes (1)
- moving tract (1)
- MRI (5)
- multibacillary (1)
- multiple myeloma (2)
- Multiple sclerosis (1)
- mumps (2)
- Murphy Sign (1)
- muscle (3)
- muscle relaxant (1)
- muscle relaxant (6)
- muscle spasm (1)
- Muscle Tension Dysphonia (1)
- muscle weakness (1)
- music therapy (1)
- mutate (1)
- myasthenia gravis (1)
- mycobacterium leprae (1)
- Myelin (1)
- myocarditis (1)
- narrowed disc space (1)
- narrowed foramina (1)
- narrowing of artery (1)
- narrowing of bronchi (1)
- nasal congestion (1)
- nasal packing (1)
- nasal polyp (1)
- nasal spray (1)
- Nasopharyngeal cancer (2)
- nasopharynx (1)
- natural (1)
- nausea (5)
- neck collars (1)
- neck rigidity. (1)
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (1)
- NEPHROTIC SYNDROME (1)
- nerve cells (1)
- nerve compression (1)
- nerve conduction test (1)
- neurological deficit (1)
- Neurological Disorders (1)
- neurotransmission (1)
- new bone (1)
- new drugs (1)
- niacin (1)
- Night Blindness (1)
- nitrosamines (1)
- Nits on scalp (1)
- no cure (1)
- no menstruation (1)
- no petechiae (1)
- nocturia (4)
- non-paralytic (1)
- non-small cell (1)
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (1)
- nose (1)
- nosebleed (2)
- NSAID (1)
- NSAIDS (3)
- numbness (1)
- Obesity (5)
- Obesity.frequent thirst (1)
- obstruction (1)
- obstruction to air flow (1)
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (1)
- odor (1)
- older adults (1)
- olecranon bursitis (1)
- open angle glaucoma (1)
- open sores (1)
- optic nerve (1)
- or penis (1)
- oral (1)
- oral diabetic medicine (1)
- oral hygience (1)
- orchitis (2)
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta (1)
- osteomalacia (1)
- Osteomyelitis (1)
- osteophytes (1)
- osteoporosis (4)
- otitis externa (1)
- otitis media (3)
- Ovarian cancer (2)
- Ovarian torsion (1)
- overactivity (1)
- overflow (1)
- overweight (1)
- oxalates (1)
- P.falciparium (1)
- P.malariae (1)
- P.ovale (1)
- P.vivax (1)
- pain (25)
- painful (3)
- painful fallopian tubes (1)
- painful menstruation (1)
- painful swollen parotid glands (1)
- painful urination (1)
- painkillers (10)
- palms (1)
- pancreatic cancer (1)
- pancreatitis (4)
- panic attacks (1)
- Papanicolaou tests Pap smear (1)
- paralysis (2)
- paralytic (1)
- parasite (1)
- parasitic (1)
- Parkinson (1)
- paromyxovirus (1)
- Paronychia (1)
- partial (1)
- paucibacillary (1)
- PECOMA (1)
- Pediculosis (1)
- peduncle (1)
- pelvic inflammatory disease (3)
- pelvic pain (2)
- pelvis (1)
- Penicillin (1)
- penile implants (1)
- penile injection (1)
- penis (2)
- peptic ulcer (1)
- perforation (1)
- Pericarditis (1)
- peritonitis (1)
- Perivascular epithelioid cell (1)
- permanent disability (1)
- Permethrin 1% cream rinse (1)
- perpheral neuropathy (1)
- persistant cold (1)
- persistent pain (1)
- pessaries (1)
- petit mal (1)
- Phalen's test (1)
- phenytoin (1)
- phlebectomy (1)
- phlebitis (1)
- phlegm (1)
- photodermatitis (2)
- phototherapy (1)
- physiotherapy (7)
- physiotheray (1)
- PID (2)
- pigmentation (1)
- piles (2)
- pimples (1)
- pityriasis capitis (1)
- Pityriasis Rosea (1)
- plane (1)
- plantar (1)
- plantar fascilitis (1)
- plaque (1)
- plasma cell (1)
- plasmapheresis (1)
- Plasmodium (1)
- Pleural Effusion (1)
- pleurodesis (2)
- pneumococcus (2)
- pneumonia (2)
- Pneumothorax (1)
- polio virus (1)
- Poliomyelitis (1)
- pollen (2)
- Polycystic kidney disease (1)
- polycystic ovarian syndrome (1)
- polycystic ovary (2)
- polyps (3)
- poor blood circulation (1)
- poor coordination (1)
- poor drainage (1)
- poor healing of skin (1)
- porphyria (1)
- post-herpetic neuralgia (1)
- Postmenopausal bleeding (1)
- pregnancy (7)
- preinvasive (1)
- Premature (1)
- Premenstrual syndrome (1)
- prepuce (1)
- preserved food (2)
- pressure and posture (1)
- pressure change (1)
- pressure on nearby organs (1)
- Prickly Heat (1)
- prickly sensation (1)
- Primary (3)
- primary health care (1)
- probe (1)
- proctocolectomy (1)
- progressive disease (1)
- prolapsed disc (1)
- prolapsed intervertebral disc (1)
- prostate (6)
- prostate cancer (1)
- prostatic fluid test. bacteria culture (1)
- Prostatitis (1)
- Protease inhibitors (1)
- protozoan (1)
- pruritus (1)
- pseudocysts (1)
- pseudomembraous enterocolitis (1)
- pseudomonas (1)
- psoriasis (1)
- psychological factor (1)
- psychological suffering (1)
- Pterygium (1)
- puberty (1)
- pulmonary embolism (1)
- purpura (1)
- pustular (2)
- pustule (1)
- pyloric stenosis (1)
- quality of life (1)
- quinines (1)
- radiation (4)
- radioactive iodine (1)
- radiofrequency ablation (1)
- radiotherapy (9)
- radiotherapy. (1)
- rare (1)
- rash (2)
- rashes and abrasions (1)
- Raynaud's Disease (1)
- rectum (1)
- recurrence (1)
- recurrent outbreaks (1)
- red (5)
- red eyes (2)
- red scaly patches (1)
- redness (2)
- reduced oxygen (1)
- reflex mechanism (1)
- regenerated cells (1)
- regenerated tissue (1)
- region (1)
- regional enteritis (1)
- Regular checkups (1)
- rehyration (1)
- reiki (1)
- relax (2)
- relaxation (1)
- relaxation techniques (1)
- renal failure (1)
- renal stones (1)
- reorganisation (1)
- rest (12)
- rest tremors (2)
- rest voice (1)
- retention of urine (1)
- retina (1)
- retinal detachment (1)
- Retinitis pigmentosa (1)
- Reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors (1)
- Reye's syndrome (1)
- rheumatoid arthritis (1)
- rhinitis (1)
- rice water diarrhoea (1)
- rifampicin (1)
- rigidity (1)
- rigors (1)
- rose spots (1)
- roseala infantum (1)
- rotablation (1)
- rotator cuff injuries (1)
- rubber band (1)
- rubella (1)
- rule of nines (1)
- runny nose (2)
- sad (1)
- Salivary Gland cancer (1)
- salivary glands (1)
- Salmonella typhi (1)
- Salpingitis (1)
- Sarcoptes Scabiei (1)
- scabicides (1)
- Scabies (1)
- Scalds (1)
- scarlet fever (2)
- schizophrenia (1)
- sciatic nerve (1)
- sciatica (3)
- sclerotherapy (1)
- scoliosis (1)
- scratch marks (1)
- scratching (1)
- scurvy (1)
- sebaceous glands (2)
- seborrheic (1)
- secondary (5)
- seizures (1)
- semen.PSA (1)
- sentinel pile (1)
- septic arthritis (1)
- septicemia (1)
- severe and prolonged joint pains (1)
- Sex linkage (1)
- sexual activity (1)
- sexual contact (1)
- sexual exposure (1)
- Sexual Health (1)
- sexually transmitted disease (9)
- shampoo (1)
- sharp object (1)
- shigella (1)
- shingles (1)
- shivering (1)
- shock (1)
- Shoulder Xray (1)
- shunt (1)
- silent killer (1)
- silvadene (1)
- simple guide (2)
- simple skin care (1)
- single (1)
- sinus blockage (1)
- sinus washout (1)
- sinuses (1)
- sinusitis (2)
- skin (13)
- skin disease (1)
- skin Polyp (1)
- skin rash (1)
- Skin scrapings (1)
- skin tags (1)
- skin trophi (1)
- sleeping sickness (1)
- slipped disc (1)
- slow development (1)
- slow movement (1)
- slow urine flow (1)
- small cell (1)
- small papules (1)
- Small red bites (1)
- small vesicle (1)
- smoking (12)
- sneezing (2)
- snoring (2)
- soaps (1)
- socks (1)
- sodium valproate (1)
- soles (1)
- sore throat (4)
- sorethroat (1)
- Spasmodic (1)
- spasticity (1)
- spectacles (1)
- speech (1)
- speech loss (1)
- spine (1)
- Spine Xray (2)
- spleen (1)
- sponging (1)
- Spontaneous (1)
- spontaneous abortion (1)
- spore forming bacterium (1)
- spread (1)
- squamous cell carcinoma (1)
- staphalococcus aureus (1)
- staphylococci (1)
- staphylococcus aureus (1)
- statins (1)
- STD (2)
- stem cells (3)
- stent (1)
- stepladder fever (1)
- steroid (2)
- Steroid or immunosuppressive drugs (1)
- steroids (3)
- stiffness (3)
- stinger (1)
- stitching (1)
- stomach cancer (1)
- stomach inflammation (1)
- Stomatitis (1)
- stones (1)
- stool blood test (2)
- stool softener (1)
- stools (1)
- stop itch and pain (1)
- strangulated hernia (1)
- streptococci (1)
- streptococcus (1)
- stress (14)
- stridor (1)
- stripping of veins (1)
- stroke (5)
- stye (1)
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (1)
- subclinical (1)
- suicide (1)
- sulfasalazine (2)
- sulphonamides (1)
- sun (1)
- sun exposure (2)
- superficial (1)
- superficial linear tear (1)
- supranuclear (1)
- sur (1)
- surgery (33)
- surgery. (1)
- surgical coning of cervix (1)
- surgical resection (1)
- sweat glands (1)
- sweet urine (1)
- swelling (6)
- swelling in abdomen (1)
- swollen blood vessels (1)
- swollen glands behind ears and neck (1)
- sympathectomy (1)
- symptomatic treatment (1)
- syncope (1)
- Syphilis (1)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosis (1)
- systolic (1)
- tachycardia (1)
- tamoxifen (1)
- tears (1)
- telbivudine (1)
- temperature change (2)
- tender (1)
- tennis elbow (2)
- Tenosynovitis (1)
- tension (2)
- Tertiary (1)
- testicular pain (1)
- Testicular torsion (1)
- testosterone (1)
- tetanus (1)
- tetanus toxoid vaccine. Triple Antigen (1)
- tetracycline (2)
- thalassaemia (1)
- Thalassemia (1)
- thenar muscle wasting (1)
- Threadmill (2)
- threadworms (2)
- thymectomy (1)
- thymus (1)
- thyroid nodules (2)
- thyroid scan (1)
- thyroxine (1)
- tic (1)
- tinnitus (4)
- tinnitus. (1)
- tiredness (1)
- tissue damage (1)
- toe nails (1)
- tonsils (1)
- tooth discoloration (1)
- toothache (1)
- torsion (1)
- tracheostomy (2)
- track (1)
- traction (1)
- tranexamic acid (1)
- Transient ischaemic attack(TIA) (1)
- trauma (2)
- Treponema pallidum (1)
- Trichomonas vaginalis (1)
- trichomoniasis (1)
- trigeminal nerve (1)
- Trigeminal Neuralgia (1)
- trigger finger (1)
- trigger points (2)
- triggers (2)
- triglycerides (1)
- trimesters (1)
- tropical sprue (1)
- trypanosomes (1)
- tumour (1)
- Turner Syndrome (1)
- TURP (1)
- tying (1)
- Type 1 (1)
- Type 2 (1)
- typhoid carrier (1)
- Typhoid Fever (1)
- ueteric stones (1)
- Ulcerative Colitis (1)
- ulcers (2)
- ultrasound (4)
- ulttasound (1)
- UNDESCENDED TESTES (1)
- unknown cause (1)
- unwashed hands (1)
- urate crystals (1)
- ureteric colic (1)
- urethitis (1)
- Urethritis (1)
- urge (1)
- urgency (1)
- uric acid (1)
- uric aid (1)
- urinary incontinence (1)
- Urinary stones (1)
- Urinary Tract infection (1)
- urine problem (1)
- urine test (3)
- urostomy (1)
- urticaria (2)
- uterine ablation (1)
- uterine causes (1)
- Uterine Fibroids (1)
- uterine prolapse (1)
- uterus prolapse (1)
- UV light (1)
- uvea (1)
- uveitis (2)
- vaccine (2)
- vagina (2)
- vagina cancer (1)
- vaginal cancer (1)
- vaginal changes (1)
- vaginal discharge (1)
- vaginal douche (1)
- vaginal soreness (1)
- varicella vaccine (1)
- varicella-zoster virus (1)
- Varicose Veins (1)
- vasomotor rhinitis (1)
- vegetarian (1)
- venogram (1)
- venous stasis (1)
- vermiform appendix (1)
- vertigo (2)
- vertigo. (1)
- vesicovaginal fistula (1)
- Viagra (1)
- Vibrio cholorae (1)
- Vincent's Angina (1)
- viral (12)
- viral infection (2)
- viral infections (1)
- virus (3)
- viruses (1)
- vision loss (2)
- Vitamin A analogues (1)
- Vitamin A Deficiency (1)
- vitamin B1 deficiency (1)
- Vitamin B12 (1)
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency (1)
- Vitamin B2 Deficiency (1)
- vitamin B3 deficiency (1)
- vitamin B5 deficiency (1)
- Vitamin B6 Deficiency (1)
- vitamin B7 deficiency (1)
- Vitamin Bs (1)
- vitamin C deficiency (1)
- Vitamin D (1)
- Vitamin E Deficiency (1)
- vitamin K (1)
- Vitiligo (1)
- vitrectomy (1)
- vocal cord cyst (1)
- vocal cord nodule (1)
- vocal cord polyp (1)
- vocal cords (1)
- vocal paralysis (1)
- voice change (1)
- vomiting (5)
- vulva (1)
- Vulvitis (1)
- wafarin (1)
- walking (1)
- warm water (1)
- warmth (1)
- warts (1)
- wash hands (1)
- wash with water (1)
- wasps (1)
- wax (1)
- weak immune system (1)
- wear and tear (1)
- webs toes of foot (1)
- weight loss (7)
- Whooping cough (1)
- Wickham's striae (1)
- Widal test (1)
- wigs (1)
- wounds (1)
- wrist splintage (1)
- wrists (1)
- X-rays (3)
- xeroderma pigmentosa (2)
- yellow fever (1)
- yellow-green vaginal discharge (1)
- yoga (1)
- young child (1)




