A Simple Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis
-----------
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
-----------
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease that can cause chronic inflammation of the joints and other areas of the body.
Who gets Rheumatoid Arthritis?
--------------------------------------
Rheumatoid Arthritis is one of the most common form of inflammatory arthritis.
It most commonly occurs between the 25 and 50 years.
However it can occur at any age.
Females are 3 times more likely to get Rheumatoid Arthritis than males.
What causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
-------------------------------------------
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease..
Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body tissues are mistakenly attacked by its own immune system which consists of cells and antibodies designed normally to "seek and destroy" invaders of the body, particularly infections.
Patients with autoimmune diseases have antibodies in their blood that target their own body tissues .
What are the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
-----------------------------------------------------------
Most common symptoms are pain, swelling, stiffness, warmth and sometimes redness of the joints.
Rheumatoid Arthritis is suspected when there are:
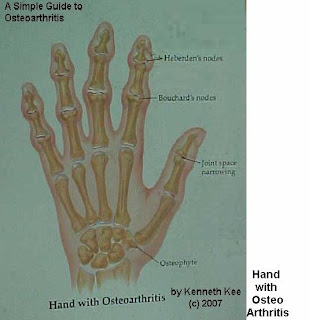
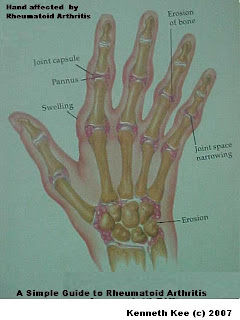
1. Swelling in the joints especially those of the hands,elbows,knees,ankles and feet.
2. Stiffness in the joints in the mornings which can last more than an hour or after prolonged rest
3.redness and warmth in one's joints
4.Persistent pain or tenderness in a joint for more than a month
5.Inability to move or use a joint normally
6. Unexplained weight loss and appetite, fatigue, or weakness together with joint pains
What tests are done to confirm Rheumatoid Arthritis?
----------------------------------------------------------------
Abnormal blood antibodies can be found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
1.A blood antibody called "rheumatoid factor" can be found in 80% of patients.
2.Another antibody called "the antinuclear antibody" (ANA) is also frequently found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
3.Another blood test that is used to measure the degree of inflammation present in the body is the C-reactive protein.
4.A blood test called the sedimentation rate (ESR) is a measure of how fast red blood cells fall to the bottom of a test tube. The sed rate is used as a crude measure of the inflammation of the joints.
The rheumatoid factor, ANA, sed rate, and C-reactive protein tests can also be abnormal in other systemic autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. Therefore, abnormalities in these blood tests alone are not sufficient for a firm diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis
How does the Rheumatoid Arthritis starts?
--------------------------------------------------
Rheumatoid Arthritis may start gradually or with a sudden and severe attack.
It usually attacks many joints at one time.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease, characterized by periods of disease flares and remissions.
Where does Rheumatoid Arthritis occur?
-------------------------------------------------
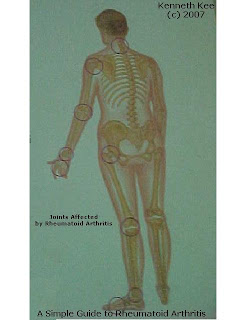
In rheumatoid arthritis, multiple joints are usually affected in a symmetrical pattern.
It most commonly affects the hands and feet,often in a systemic pattern(both right and left joints are affected).
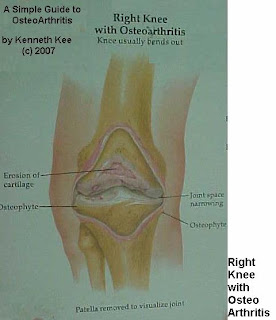
Other joints affected are the elbow,knees,and ankles.
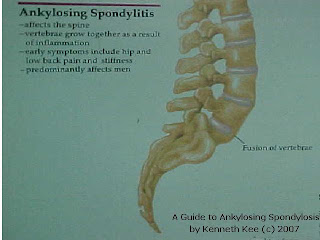
Less common are shoulder,hip and spine.
What are the Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
----------------------------------------------------------------
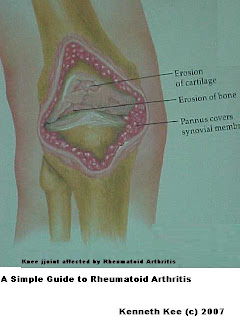
Rheumatoid Arthritis can result in joint deformities and disability especially in untreated severe cases.
Daily activities such as bathing,dressing, walking and even writing may be difficult.
Besides the joints, Rheumatoid Arthritis may sometimes affect other organs such as the eyes,lungs,skin,intestines,nerves and bone marrow.
Mild fever, fatigue, loss of appetite and loss of weight may be present.
Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis is associated with an incresed risk of mortality.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis treated?
--------------------------------------------
There is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis.
Therefore the purpose of treatment is to:
1. improve functions and
2. reduce pain and discomfort.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis can be broadly classified into:
1. Non-drug therapy:
Weight loss is an effective way to reduce the stress on the joints and minimise the pain Walking sticks are useful ways to offload the stress on the affected weight bearing joints such as hips or knee.
Hot packs are useful aids in the morning to soften a stiff arthritic joint whereas braces and knee guards are useful supports to give some comfort to the knee.
Exercises that improve strength, agility and flexibilty are useful to minimise the disability of Rheumatoid Arthritis. A range of motion exercises is useful to keep the joints supple and mobile.
Water based exercises are a good alternative form of aerobic workout by patients afflicted by Rheumatoid Arthritis. The warm water especially is a good medium for joint mobility and together with the buoyancy of water it helps to minimse the body weight impact on the joints.
2. Drug therapy
There are 2 main types of drugs:
1. symptom modifying helps to alleviate the symptoms but do not change the natural history of the conditions. Examples are Non-steroidal Anti-inflamatory Drugs(NSAIDS) like diclofenac.
2. disease modifying drugs such as steroids, methothrexate, sulphasalazine, redaura, hydroxychloroquine have been shown to slow down the damage caused by Rheumatoid Arthritis. However they cause a lot of side effects such as anemia, abnormal white cells, kidney damage,liver damage, vision loss so the medications must be monitored all the time.
It is important that the disease should be controlled before irreversible joint damage occurs.
Newer "second-line" drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis include leflunomide (Arava), and the "biologic" medications etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), anakinra (Kineret), and adalimumab (Humira).
3. Surgery
Surgery is used as a last result to correct deformities and reduce disability.
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis optimally involves a combination of patient education, rest and exercise, joint protection, medications, and occasionally surgery.
Early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis results in better outcomes.
-----------
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
-----------
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease that can cause chronic inflammation of the joints and other areas of the body.
Who gets Rheumatoid Arthritis?
--------------------------------------
Rheumatoid Arthritis is one of the most common form of inflammatory arthritis.
It most commonly occurs between the 25 and 50 years.
However it can occur at any age.
Females are 3 times more likely to get Rheumatoid Arthritis than males.
What causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
-------------------------------------------
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease..
Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body tissues are mistakenly attacked by its own immune system which consists of cells and antibodies designed normally to "seek and destroy" invaders of the body, particularly infections.
Patients with autoimmune diseases have antibodies in their blood that target their own body tissues .
What are the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
-----------------------------------------------------------
Most common symptoms are pain, swelling, stiffness, warmth and sometimes redness of the joints.
Rheumatoid Arthritis is suspected when there are:
1. Swelling in the joints especially those of the hands,elbows,knees,ankles and feet.
2. Stiffness in the joints in the mornings which can last more than an hour or after prolonged rest
3.redness and warmth in one's joints
4.Persistent pain or tenderness in a joint for more than a month
5.Inability to move or use a joint normally
6. Unexplained weight loss and appetite, fatigue, or weakness together with joint pains
What tests are done to confirm Rheumatoid Arthritis?
----------------------------------------------------------------
Abnormal blood antibodies can be found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
1.A blood antibody called "rheumatoid factor" can be found in 80% of patients.
2.Another antibody called "the antinuclear antibody" (ANA) is also frequently found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
3.Another blood test that is used to measure the degree of inflammation present in the body is the C-reactive protein.
4.A blood test called the sedimentation rate (ESR) is a measure of how fast red blood cells fall to the bottom of a test tube. The sed rate is used as a crude measure of the inflammation of the joints.
The rheumatoid factor, ANA, sed rate, and C-reactive protein tests can also be abnormal in other systemic autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. Therefore, abnormalities in these blood tests alone are not sufficient for a firm diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis
How does the Rheumatoid Arthritis starts?
--------------------------------------------------
Rheumatoid Arthritis may start gradually or with a sudden and severe attack.
It usually attacks many joints at one time.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease, characterized by periods of disease flares and remissions.
Where does Rheumatoid Arthritis occur?
-------------------------------------------------
In rheumatoid arthritis, multiple joints are usually affected in a symmetrical pattern.
It most commonly affects the hands and feet,often in a systemic pattern(both right and left joints are affected).
Other joints affected are the elbow,knees,and ankles.
Less common are shoulder,hip and spine.
What are the Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
----------------------------------------------------------------
Rheumatoid Arthritis can result in joint deformities and disability especially in untreated severe cases.
Daily activities such as bathing,dressing, walking and even writing may be difficult.
Besides the joints, Rheumatoid Arthritis may sometimes affect other organs such as the eyes,lungs,skin,intestines,nerves and bone marrow.
Mild fever, fatigue, loss of appetite and loss of weight may be present.
Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis is associated with an incresed risk of mortality.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis treated?
--------------------------------------------
There is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis.
Therefore the purpose of treatment is to:
1. improve functions and
2. reduce pain and discomfort.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis can be broadly classified into:
1. Non-drug therapy:
Weight loss is an effective way to reduce the stress on the joints and minimise the pain Walking sticks are useful ways to offload the stress on the affected weight bearing joints such as hips or knee.
Hot packs are useful aids in the morning to soften a stiff arthritic joint whereas braces and knee guards are useful supports to give some comfort to the knee.
Exercises that improve strength, agility and flexibilty are useful to minimise the disability of Rheumatoid Arthritis. A range of motion exercises is useful to keep the joints supple and mobile.
Water based exercises are a good alternative form of aerobic workout by patients afflicted by Rheumatoid Arthritis. The warm water especially is a good medium for joint mobility and together with the buoyancy of water it helps to minimse the body weight impact on the joints.
2. Drug therapy
There are 2 main types of drugs:
1. symptom modifying helps to alleviate the symptoms but do not change the natural history of the conditions. Examples are Non-steroidal Anti-inflamatory Drugs(NSAIDS) like diclofenac.
2. disease modifying drugs such as steroids, methothrexate, sulphasalazine, redaura, hydroxychloroquine have been shown to slow down the damage caused by Rheumatoid Arthritis. However they cause a lot of side effects such as anemia, abnormal white cells, kidney damage,liver damage, vision loss so the medications must be monitored all the time.
It is important that the disease should be controlled before irreversible joint damage occurs.
Newer "second-line" drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis include leflunomide (Arava), and the "biologic" medications etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), anakinra (Kineret), and adalimumab (Humira).
3. Surgery
Surgery is used as a last result to correct deformities and reduce disability.
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis optimally involves a combination of patient education, rest and exercise, joint protection, medications, and occasionally surgery.
Early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis results in better outcomes.