A Simple Guide to Cervicitis
----------------------------------------------------
What is Cervicitis?
---------------------------------------
Cervicitis is non-specific infection of the cervix.
It is most common on the posterior cervix but may be anterior or concentric.
Who is affected by Cervicitis?
---------------------------------------------------
1.Congeital cervical erosions or cervicitis can occur in virgins.
2.sexually active females
3.dilatation in labor or during abortion
What are the types of Cervicitis?
-------------------------------------------
1.Simple:
Erosion surface is smooth
2.Papillary:
Erosion surface is rough
3.Follicular:
Erosion surface is cystic
What are the Causes of Cervicitis?
-----------------------------------------------------
Bacterial infections:
---------------------------
1.Gonorrhea
2.Chlamydia
3.staphylococcus aureus
4.Streptococcus
5.Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
6.E.coli
Viral infections:
--------------------------
1.Genital herpes
2.Human Papilloma Virus
Other causes:
--------------------
1.Cervical cap
2.Device to support the uterus (pessary)
3.Diaphragm
4.allergy to spermicides
5.Exposure to a chemical
What are the complications of Cervicitis?
---------------------------------------------------
1.Pelvic inflammatory disease
2.Urethritis and cystitis
3.rarely malignant changes in cervix
4.inguinal lymphadenitis
5.Cervical cancer
What are the Symptoms and signs of Cervicitis?
-----------------------------------------------------------
1.Mucopurulent vaginal discharge (Gray, white, or yellow color) with odor
2.Blood in the vaginal discharge
a.After intercourse
b.After menopause
c.Between periods
3.Urinary infection symptoms - frequency and pain
3.hematuria (blood in the urine)
4.Pelvic pain
5.Backache
6.Painful sexual intercourse
7.Pain in the vagina
8.Pressure or heaviness in the pelvis
Signs:
1.reddened area of cervix
2.erosion of cervical wall
3.Vaginal surface of cervix may be affected
4.pus discharge from the cervix
5.Swelling (inflammation) of the walls of the vagina
How is diagnosis of Cervicitis made?
-----------------------------------------------
1.Vaginal examination with Pap's smear of cervical cells
2.Cervical swab for culture and sensitivity to antibiotics
3.Blood tests( white cell count , blood culture, chlamydia, gonorrhea)
4.Biopsy of cervical erosions.
What is the treatment of Cervicitis?
---------------------------------------------------
1. Antibiotics is given according to the sensitivity of bacteria in the culture.
2.Pelvic pain and backache may be treated with paracetamol
3.Local application of sulphonamide, tetracycline or other antibiotic cream to affected cervical area
4.Electro-Cauterisation of the affected cervical area
5.Cryosurgery of cervical erosions
6.Cone biopsy if necessary of affected cervix area.
7.Hormonal therapy (especially in postmenopausal women)
8.Laser therapy of cervical erosions
What is the prognosis of Cervicitis?
-------------------------------------------------------------
Prognosis with appropriate treatment and antibiotics is generally good.
Recurrence is common.
Cervicitis may last for months to years.
Cervicitis may lead to pain with intercourse (dyspareunia).
What are Preventive measures for Cervicitis?
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Avoid sexual intercourse with multiple partners.
Use condoms during sexual intercourse.
Vaccination against human papilloma virus
Avoid chemical irritants such as douches and deodorant tampons.
Avoid using spermicidal contraceptives
Make sure that any foreign objects that inserted into the vagina is clean or sterile
Showing posts with label pelvic pain. Show all posts
Showing posts with label pelvic pain. Show all posts
Wednesday, September 17, 2008
Monday, September 24, 2007
A Simple Guide to Ovarian Cancer
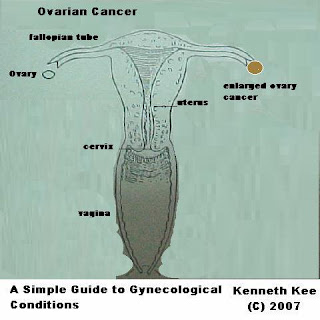
A Simple Guide to Ovarian Cancer
--------------
What is Ovarian Cancer?
----------------
--------------
What is Ovarian Cancer?
----------------
Ovarian Cancer is a disease which cause abnormal cells in the ovary to proliferate and spread to the rest of the ovary or outside the ovary.
What are the different types of Ovarian Cancer?
-------------------------------------------------
Most experts group ovarian cancers within three major categories, according to the kind of cells from which they were formed:
1.epithelial tumors arise from cells that line or cover the ovaries;
2.germ cell tumors originate from cells that are destined to form eggs within the ovaries; and
3.sex cord-stromal cell tumors begin in the connective cells that hold the ovaries together and produce female hormones.
The most common type, the epithelial carcinoma, that begins from the surface of the ovary is discussed here.
Who is at risk of Ovarian Cancer?
---------------------------------------
The cause of cancer of the ovary is unknown.
However, studies show that certain factors may increase the chance of developing this disease. 1.family history of ovarian cancer.
2.history of cancer of the breast or colon.
3.age over 60 years.
4. Infertility or not having children. The more children you have, the lesser your risk is.
5.Early menstruation before the age of 12
6.late menopause
7.high fat diet
8.Use of fertility drugs, or Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT).
Attempts are being made to detect early stages of ovarian cancer, especially among women who have an increased risk. A blood test is done to check for a substance called CA 125.
If the sample contains raised amounts of CA 125, an ultrasound scan may be done to see if your ovaries appear abnormal in any way.
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
---------------------------------------------------
Ovarian cancer is the most dangerous of gynaecological cancers because it is often silent and difficult to detect.There is no early detection method, so you must be vigilant and take note of persistent warning signs seriously.
If you are having some of the following symptoms persisting for more than a week or so, see your doctor.
1.Vague gastrointestinal symptoms such as gas, indigestion, nausea and a bloated feeling
2.Swelling in the abdomen, unexplained weight gain
3.Pelvic or abdominal pain or discomfort, and/or feeling of fullness
4.Urinary symptoms e.g. frequency and/or urgency of urination in the absence of an infection
5.Unexplained or changes in bowel habits
6.Loss of appetite/loss of weight
7.backache or pain inthe legs
8.Abnormal vaginal bleeding, although this is rare
If you do have any of the above symptoms you must have them checked by your doctor. Remember, they are non specific and most women with these symptoms will not have cancer.
How do you make the diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer?
-----------------------------------------------------------
If you are at risk of ovarian cancer, see your gynaecologist regularly.
The following may be done:
recto-vaginal bimanual pelvic exam,
recto-vaginal bimanual pelvic exam,
Pap smear,
blood test for CA-125
transvaginal ultrasound
What are the treatment of Ovarian Cancer?
---------------------------------------------------
Treatment depends on a number of factors, including the stage of the disease (the extent of spread of the disease) and the general health of the patient.
Surgery, chemotherapy and various types of radiotherapy may be used alone, or in combination to treat ovarian cancer.
What are the treatment of Ovarian Cancer?
---------------------------------------------------
Treatment depends on a number of factors, including the stage of the disease (the extent of spread of the disease) and the general health of the patient.
Surgery, chemotherapy and various types of radiotherapy may be used alone, or in combination to treat ovarian cancer.
Surgery
Surgery is normally the first choice of treatment for ovarian cancer, and may sometimes also be needed to make the diagnosis. If detected is in the early stages, surgery is all the treatment that may be required. The ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and cervix are usually removed. The omentum and lymph nodes in the abdomen are often removed too.
If the surgeon feels the cancer may be difficult to remove, a few cycles of chemotherapy may be applied first and surgery carried out thereafter, in the hope that the tumour would have been reduced.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be given to destroy any cancerous cells that may remain in the body after surgery, to control cancer growth or to relieve symptoms of the disease. Sometimes a few cycles of chemotherapy may have to be applied before surgery is carried out.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is less commonly used in this cancer but may sometimes be used to treat individual areas of cancer which have recurred after surgery and chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be given to destroy any cancerous cells that may remain in the body after surgery, to control cancer growth or to relieve symptoms of the disease. Sometimes a few cycles of chemotherapy may have to be applied before surgery is carried out.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is less commonly used in this cancer but may sometimes be used to treat individual areas of cancer which have recurred after surgery and chemotherapy.
There have been many reports of the potential benefits of hormone treatments in patients with ovarian cancer that does not respond to conventional therapy.
Some patients with treatment-resistant (refractory) epithelial cancers have been treated with:
1.progestins - crude forms of the female sex hormone progesterone;
1.progestins - crude forms of the female sex hormone progesterone;
2.estrogens - for example, diethylstilbestrol
3.combination estrogen/progestin therapy;
4.antiestrogens - tamoxifen;
5.androgens - male sex hormones for example, Halotestin
6.gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) - a hormone of the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of ovary-related hormones from the pituitary gland.
3.combination estrogen/progestin therapy;
4.antiestrogens - tamoxifen;
5.androgens - male sex hormones for example, Halotestin
6.gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) - a hormone of the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of ovary-related hormones from the pituitary gland.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy eventually may provide some control over cancer susceptibility and its treatment. Ovarian cancer, like all cancers, is believed to result from a build-up of genetic defects within the cells.Genetic engineers hope to correct such damage by transplanting copies of normal genes into cells with genetic defects. However at the moment gene therapy is still experimental.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Subscribe Now: Feed Icon
Clicktale
Labels
- abdominal pain (10)
- abnormal brain signals (1)
- abscess (1)
- Achilles tendinitis (1)
- acid reflux (2)
- acne (1)
- Acne Rosacea (1)
- Acoustic neuroma (1)
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (1)
- acyclovir (2)
- ADDISON DISEASE (1)
- Adenoidectomy (1)
- Adenoiditis (1)
- Adenoids (1)
- Aedes mosquitoes (2)
- aerobics (1)
- aging (2)
- AIDS (2)
- air conditioners (1)
- alcohol (5)
- Alcoholism (1)
- allergens (2)
- allergies (1)
- allergy (2)
- alopecia (1)
- alzeheimer's disease (1)
- amblyopia (2)
- amebiasis (1)
- Amenorrhea (1)
- amylotrophic lateral sclerosis (1)
- anaemia (4)
- anaerobic bacteria (2)
- Anal fissure (1)
- Anal Fistula (1)
- analgesic (4)
- androgens (1)
- ANDROPAUSE (1)
- anger management (1)
- Angiogram (1)
- ankles (1)
- anopheles mosquito (1)
- anorectal abscess (1)
- anovulation (1)
- Answers (3)
- Anthrax (1)
- anti-aging (1)
- anti-diarrhoea (1)
- anti-flatulent (1)
- antibiotic (8)
- Antibiotic therapy (1)
- antibiotics (26)
- anticholinesterase (1)
- anticoagulant (1)
- antidepressant (1)
- antifungal (3)
- antihistamine (4)
- antimycotics (1)
- antioxidants (1)
- antispasmodic (2)
- Antispasmodics (1)
- antitoxins (1)
- antiviral (1)
- anus (2)
- anxiety (2)
- aphthous ulcers (1)
- Appendicitis (1)
- appendix perforation (1)
- appetite suppressant (1)
- areflexia (1)
- artane (1)
- Artery blockage (1)
- arthritis (4)
- articular cartilage injury (1)
- asbestos (1)
- aspiration (2)
- aspirin (1)
- asthma (1)
- Astigmatism (1)
- atherosclerosis (1)
- Athlete's Foot (1)
- atopic dermatitis (1)
- atopic eczema (2)
- atrial fibrillation (2)
- atrophic vaginitis (1)
- aural toilet (1)
- autoimmune disease (3)
- autoimmune neuromuscular disease (1)
- autonomic dysfunction (1)
- avitaminosis (1)
- avoid causative substance (1)
- avoid prolonged standing ulcers (1)
- avoid rubbing (1)
- avoid straining (1)
- avoid sudden movement (1)
- avoid touching the acne (1)
- axilla (1)
- back pain (1)
- Backache (2)
- Baclofen (1)
- bacteria (15)
- bacteria culture (4)
- bacterial (4)
- bacterial infection (6)
- bacterial vaginosis (1)
- bad posture (1)
- baking soda (1)
- Balanitis (1)
- ballooning (1)
- ballooning of blood vessel in brain (1)
- barking cough (1)
- bartholin cyst (1)
- basal cell carcinoma (1)
- Basal ganglia (1)
- bed bugs (1)
- bed sores (1)
- Bedding and clothing (1)
- bedwetting (2)
- bees (1)
- Beestings (1)
- Bence Jones (1)
- benign (3)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (1)
- Benzyl Benzoate lotion (1)
- Besy ahoo answer (1)
- beta blockers (1)
- biological targeted therapy. (1)
- biological warfare (1)
- biopsy (4)
- bipolar disorders (1)
- bipolar disorders treatment (1)
- bird flu (1)
- birth control (1)
- birth control methods (1)
- bladder cancer (3)
- bleeding (6)
- bleeding disorder (2)
- bleeding ulcers (1)
- Blepharitis (1)
- blindnes (1)
- blindness (4)
- blisters (3)
- bloating (5)
- blocked nose or ear (1)
- blocked opening of glands (1)
- Blood blockage (2)
- blood cancer (2)
- blood in sputum (1)
- blood in urine (2)
- blood loss (1)
- blood pressure (1)
- blood release (1)
- blood transfusion (2)
- bloodborne infection (1)
- blurred vision (4)
- BMI (1)
- bodyache (2)
- bone density test (1)
- bone fusion (1)
- bone infection (1)
- bone marrow transplant (3)
- bone pain (1)
- Bordetella pertussis (1)
- bowel movement (1)
- BPH (1)
- brace (1)
- bradyacardia (1)
- brain damge (1)
- brain infections (2)
- brain tumour (2)
- breast (1)
- breast cancer (1)
- breathless (6)
- brittle bones (1)
- broken blood vessels (1)
- Bronchitis (1)
- bronchodilator (2)
- bronchoscopy (1)
- bruise (1)
- BSE (1)
- Buerger's Disease (1)
- bulbar (1)
- burn calories (3)
- burning sensation (1)
- Burns (1)
- burrow lines on the skin (1)
- buttocks (1)
- CA 125 (1)
- calcium (1)
- calcium supplements (1)
- cancer (9)
- cancer of the cervix (1)
- cancer of vulva (1)
- Cancer screening (5)
- cancers (1)
- Candida albicans (2)
- Candidiasis (1)
- Carbamazepine (1)
- carbohydrate diet (1)
- cardiac tamponade (1)
- cardiogenic shock (1)
- cardiovascular collapse (1)
- cardioversion (2)
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (1)
- CAT Scan (1)
- cataract (1)
- Caudate nucleus (1)
- cautery (1)
- CD4 (T-cell) lymphocytes (1)
- Cellulitis (1)
- Central nervous system (1)
- cerebral aneurysm (1)
- cerebral palsy (1)
- cerebrovascular accident(CVA) (1)
- cervical cancer (2)
- Cervical Spondylosis (1)
- cervicitis (2)
- cervix cancer (1)
- cessation of menstruation (1)
- chalazion (1)
- changes in personality and behaviour (1)
- chemical treatment (1)
- chemicals (7)
- chemotherapy (10)
- chickenpox (2)
- chikungunya fever (1)
- child school problems (1)
- childhood (1)
- chills (1)
- Chlamydia (1)
- Cholecystectomy (1)
- Cholecystitis (2)
- Cholera (1)
- cholesterol (2)
- Choreia (disease) (1)
- choroid (2)
- chronic (4)
- chronic bronchitis (1)
- chronic fatigue (1)
- chronic illness (2)
- Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (2)
- chronic pelvic pain. endometrosis (1)
- chronic suppurative otitis media (1)
- Cialis (1)
- cigarettes (1)
- ciliary body (1)
- ciprofloxacin (1)
- circumcision (1)
- cirrhosis.cold compress (2)
- cleaning (1)
- clofazimine (1)
- closed angle glaucoma (1)
- clusters (2)
- coccyx injury (1)
- cochlea (1)
- Coeliac Disease (1)
- cold compress (3)
- cold sores (1)
- cold temperatures (1)
- colic (1)
- collagen abnormalities (1)
- colon (1)
- colon cancer (1)
- colonoscopy (1)
- common (1)
- common cold (1)
- compression (2)
- compression of the median nerve (1)
- Conditions and Diseases (2)
- condoms (1)
- congenital (3)
- congenital deformities (1)
- congestion (1)
- congestive heart failure (1)
- conjuctivitis (2)
- conjuntiva (1)
- constipation (5)
- contact dermatitis (1)
- contact lens (4)
- contagious (1)
- contaminated food (2)
- contaminated soil (1)
- contaminated water and food (1)
- contents (1)
- contraction of the diaphragm (1)
- control diet (2)
- contusion (1)
- convulsions (1)
- cornea (1)
- corneal blockage (1)
- corneal ulcer (2)
- coronary artery bypass graft surgery (1)
- Coronary Heart Disease (1)
- corticosteroid creams (2)
- corticosteroid injections. (1)
- corticosteroids (3)
- cortisone injections (1)
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae (1)
- cough (7)
- CPAP (1)
- cramps (1)
- Crohn's Disease (1)
- crooked spine (1)
- Croup (1)
- CSF (1)
- curvature (1)
- CUSHING SYNDROME (1)
- cut (1)
- Cutaneous (1)
- Cutaneous Larva migrans (1)
- cystine (1)
- cystitis (1)
- cystoscopy (2)
- Cytomegalovirus (1)
- Dandruff (1)
- danger in pregnant mothers (1)
- danger of kidney and heart problems (2)
- dapsone (1)
- De Quarvian's Disease (1)
- deafness (3)
- decongestant (1)
- deep vein thrombosis (2)
- deformities (1)
- degree (1)
- dehydration (3)
- dementia (2)
- Demyelinating Diseases (1)
- dengue (1)
- Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever (1)
- Dengue Shock Syndrome (1)
- dental caries (1)
- dental hygiene (1)
- dental pain (1)
- Dental problems (1)
- depression (5)
- dermatophytes (1)
- desensitisation (1)
- diabetes (7)
- diabetes insipus (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus (2)
- dialysis (1)
- dialysis or transplant (1)
- diarrhea (6)
- diarrhoea (1)
- diastolic (1)
- diet (5)
- difficult breathing (1)
- diphenhydramine (1)
- Diphtheria (1)
- disability (1)
- discharge (1)
- discharge fom penis or vagina (1)
- dislocation of elbow (1)
- dislocation of shoulder (1)
- disorientation (1)
- diuretic (1)
- Diverticulitis (1)
- Diverticulosis (1)
- dizziness (1)
- dopamine transmitter (1)
- Down's Syndrome (2)
- drainage of pus (1)
- dribbling (2)
- drink more water (1)
- drug addict counselling (1)
- drug addicts (1)
- drugs (4)
- dry (3)
- drying agents (1)
- dryness (1)
- DTP vaccine (2)
- Duchenne (1)
- duchenne muscle dystrophy (1)
- DUPUYTREN'S CONTRACTURE (1)
- dust (3)
- dust mites (1)
- dysentery (2)
- Dysmenorrhea (1)
- dyspepsia (1)
- dysphagia (2)
- ear canal polyp (1)
- ear infections (1)
- ear pain (1)
- ear tugging (1)
- earache (1)
- earlobe infection (1)
- early 20 (1)
- eating disorders (1)
- ecchymosis (1)
- ECG (1)
- ectopic pregnancy (1)
- ECU tendonitis (1)
- Eczema (1)
- edema (1)
- elastic stockings (1)
- electricity (1)
- electrocardiogram (1)
- emergency (5)
- EMG (1)
- emotional (1)
- emphysema (1)
- encephalitis (3)
- endometrial tissues (1)
- Endometriosis (2)
- enlarged liver (1)
- enlarged liver and spleen (1)
- enlarged lymph nodes (2)
- enlarged neck nodes (1)
- enlarged tonsils (2)
- enlarged uterus (1)
- entecavir (1)
- enteric virus (1)
- Entropion (1)
- enuresis (2)
- Epididymitis (1)
- epiglottis flip backwards (1)
- epilepsy (1)
- epistaxis (1)
- Epstein-Barr virus (3)
- Erectile dysfunction (1)
- erosions (1)
- erythrodermic (1)
- erythromycin (1)
- essential (1)
- eustachian tubes (1)
- excess thyroid hormones (1)
- Excessive Menstrual Bleeding (1)
- excessive use of voice (1)
- excessive vaginal bleeding (1)
- exercise (8)
- extent (1)
- eye (1)
- eye injuries (1)
- eye ointment (1)
- eye pain (1)
- eye protection (1)
- eye strain (1)
- eyedrops (2)
- eyelashes (1)
- eyepads (1)
- eyes (1)
- facial massage (1)
- facial palsy (1)
- family history (2)
- Family Medical Doctor (40)
- fast growing (1)
- fast heart beat (1)
- fast heartbeats (1)
- fat absorption suppressant (1)
- fatigue (2)
- fear (1)
- female hormones (1)
- female predominance (1)
- fever (22)
- fiber (1)
- fibrates (1)
- fibre (1)
- fibroid (1)
- fibroids (1)
- Fibromyalgia (2)
- fibrosis (1)
- fibrous tissue (2)
- filiform (1)
- Finasteride (1)
- finger nails (1)
- fish skin (1)
- fits (1)
- flat foot (1)
- fluid (1)
- fluids (3)
- foetal development (1)
- folic acid (1)
- folic acid deficiciency (1)
- Folliculitis (2)
- food allergy (1)
- food triggers (1)
- Foot and Mouth Disease (1)
- Foot care (2)
- footwear (1)
- foreign bodies (2)
- forgetfulness (1)
- fracture (1)
- fractures (2)
- frequency (4)
- frequent cystitis (1)
- frequent urine (1)
- Frozen Shoulder (1)
- full stomach (1)
- functional (1)
- functional disorder (1)
- fungal (4)
- fungi infection (1)
- fungus (1)
- fungus Malassezia furfur (1)
- fusion (1)
- g6pd deficiency (1)
- Gait abnormality (1)
- gallbladder (1)
- gallbldder (1)
- gallstone (1)
- gallstones (1)
- ganglion (1)
- ganglion cyst (1)
- gangrene (2)
- gas (1)
- gastritis (2)
- gastroscopy (2)
- generalised rash (4)
- genes (2)
- genetic (8)
- genetic factor (2)
- genetics (1)
- Genital Herpes (1)
- genital warts (1)
- gerd treatment (2)
- german measles (1)
- Gestational diabetes (1)
- giant cell arteritis (1)
- giardiasis (2)
- giddiness (1)
- giddy (1)
- Gingivitis (1)
- glans (1)
- glass (1)
- glaucoma (1)
- Glomerulonephritis (1)
- Glossitis (1)
- Gluten Enteropathy (1)
- goiter (1)
- good dental hygiene (1)
- good posture (1)
- gout (1)
- gradual onset (1)
- gram negative bacteria (1)
- gram positive (1)
- grand mal (1)
- grayish tonsillar exudate (1)
- groins (1)
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome (1)
- gum boils (1)
- guttate (1)
- gynecologic cancer (1)
- gynecological cancer (1)
- Gynecomastia (1)
- hair follicles (1)
- hair loss (1)
- hair transplant (1)
- hair weaving (1)
- Halitosis (1)
- hallux vulgus (1)
- halos (1)
- Hand (1)
- hand hygiene (1)
- hard large stools (1)
- harden stools (1)
- hasty swallowing of food or air (1)
- HBV virus infection (1)
- HCV (1)
- HCV antibodies (1)
- HDL (1)
- head injury (2)
- headache (10)
- Health (1)
- Health education (2)
- health issues (1)
- healthy life stye (1)
- healthy lifestyle (6)
- hearing loss (1)
- heart (1)
- heart attack (1)
- heart disease (1)
- heartburn (2)
- heat (1)
- Heat Stroke (1)
- heel pads (1)
- Helicobacter pylori (2)
- heliobactor pylori (1)
- helpless (1)
- hemophilia (1)
- hemorrhage (1)
- HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA (2)
- Hepatitis (1)
- Hepatitis A (1)
- hepatitis A virus(HAV) (1)
- hepatitis B (2)
- Hepatitis C (1)
- hepatitis virus (1)
- hepatitis. (2)
- hepatocytes (1)
- herald patch (1)
- hereditary (7)
- herniorrhaphy (1)
- herpes virus (1)
- herpes zoster (1)
- hiatus hernia (1)
- hiccup (1)
- high blood pressure (1)
- high cholesterod (1)
- high cholesterol (1)
- high level (1)
- high mortality (2)
- high protein food (1)
- hips (1)
- histamine (1)
- HIV (2)
- HMB-45-positive (1)
- HMF (1)
- holes (1)
- hormonal (2)
- hormonal imbalance (1)
- hormone (3)
- Hormone replacement therapy (1)
- hormone treatment (1)
- hornets (1)
- hot flushes (1)
- HPV (1)
- HPV DNA test (1)
- HRT (1)
- HSV1 (1)
- HSV2 viruses (1)
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (1)
- Human papilloma virus Infection (1)
- human papillomavirus (2)
- Huntington (1)
- Huntington's disease (1)
- Hydrocoele (1)
- hypercalcemia (1)
- hyperextended knees (1)
- Hyperhidrosis (1)
- HYPERKALEMIA (1)
- hypernatremia (1)
- hyperparathyroidism (1)
- Hypertension (4)
- Hyperthyroid Disease (1)
- hypnotherapy (1)
- hypocalcemia (1)
- hypokalemia (1)
- hyponatremia (1)
- hypoparathyroidism (1)
- hypothyroid (1)
- hypothyroidism (1)
- hysterectomy (1)
- i/v fluids (1)
- Ichthyosis (1)
- IgM antibodies (1)
- immature blood cells (1)
- immunosuppressant (1)
- immunotherapy (2)
- Impetigo (1)
- incised and drained (1)
- index by labels (1)
- infected crust (2)
- infected oil gland (2)
- infection (4)
- infection. hair follicle (1)
- infections (7)
- infectious (3)
- Infectious Mononucleosis (1)
- infertility (3)
- infertility. (1)
- inflammation (7)
- inflammation of airway (1)
- inflammation of the mouth (1)
- influeza (3)
- infranuclear (1)
- Inguinal hernia (1)
- inhalation (1)
- inherited (1)
- inherited blood clotting (1)
- injection (1)
- injuries (1)
- injury (8)
- insects (1)
- insomnia (1)
- insufficient blood flow (1)
- insufficient haemaglobin (1)
- insulin (2)
- interferon (1)
- intermittent claudication (1)
- Intertrigo (1)
- intestinal (2)
- intestinal perforation (1)
- intestines (1)
- intraocular pressure (1)
- intrauterine device (1)
- intussusception (1)
- invasive (2)
- inverse (1)
- iris (1)
- iron (1)
- irregular meals (1)
- irregular menses (1)
- irregular rhythm (1)
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (1)
- irritants (1)
- irritation (1)
- isorbide (1)
- itch (6)
- Itchiness (1)
- itching (2)
- itchy (2)
- itchy nose (1)
- IUD (1)
- jaundice (5)
- joint pain (1)
- joints (2)
- KAWASAKI DISEASE (1)
- keloid (1)
- kidney (2)
- Kidney cancer (1)
- kidney damage (1)
- kidney disease (3)
- Klinefelter's Syndrome (1)
- Knee cap dislocation (1)
- knee ligaments injury (1)
- knee Xray (1)
- knees (1)
- knock (1)
- Koplik's spots (1)
- laceration (1)
- lactobacillus bacteria (1)
- laminectomy (1)
- lamivudine (1)
- laparoscope (1)
- lapband (1)
- Laryngeal cancer (1)
- Laryngitis (1)
- laryngopharyngeal reflux (1)
- Laryngx (1)
- laser (1)
- laser coagulation (1)
- laser surgery (1)
- LASIK (1)
- LASIK surgery (1)
- late teen (1)
- latent (1)
- LDL (1)
- leg (1)
- Legionnaire's Disease (1)
- lens transplant (1)
- leprosy (1)
- leptospirosis (2)
- leucocytosis (1)
- leukemia (1)
- levadopa (1)
- Levitra (1)
- Lice (1)
- lichen planus (1)
- life threatening (1)
- lifelong (2)
- ligamentous sheath (1)
- light sensitivity (1)
- limping (1)
- lipids (1)
- lipoma (1)
- liposarcoma (1)
- liposuction (1)
- Little's area (1)
- liver (1)
- liver cancer (3)
- Liver Cirrhosis (2)
- liver dysfunction. (1)
- Longo technique (1)
- loose ligaments (1)
- lose weight (3)
- loss in life events (1)
- loss of appetite (3)
- loss of memory (1)
- loss of mobilty (1)
- lots of water (1)
- low calcium (1)
- low fibre (1)
- low level (1)
- low oestrogens (2)
- low platelets (1)
- low thyroid (1)
- low Vitamin D (1)
- lower abdominal cramp (1)
- lower abdominal pain (1)
- lower immunity (1)
- lumbar spinal stenosis (1)
- lump (1)
- lump in neck (1)
- lung cancer (2)
- lymph node enlargement (1)
- lymph nodes (2)
- lymphatic system (1)
- lymphocytes (1)
- lymphoma (2)
- M proteins (1)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (1)
- maic attacks (1)
- major cosmetic surgery (1)
- malaria (1)
- Malathion 0.5% lotion (1)
- male baldness (1)
- MALE MENOPAUSE (1)
- malignant (3)
- mammogram (1)
- mandibular branches (1)
- marfan's syndrome (1)
- massage therapy (1)
- mast cells stimulant (1)
- Mastitis (1)
- maxillary (1)
- McBurney's Point (1)
- measles (2)
- Medical case Studies (125)
- medical conditions (5)
- medication side effects (2)
- medications (3)
- medicine (1)
- medicines (2)
- meditation (2)
- megacolon (1)
- melanin (1)
- melanoma (1)
- memory loss (1)
- men (1)
- Meniere's Disease (1)
- meningitis (2)
- meningococcus (1)
- meniscus tears (1)
- menopause (3)
- menorrhagia (3)
- mental illness (1)
- mental retardation (1)
- metal (1)
- methotrexate (1)
- metronidazole (1)
- migraine (1)
- mild fever (1)
- mildly contagious (1)
- minoxidil (1)
- miscarriage (1)
- MMR vaccine (3)
- moist (1)
- moisturizer (1)
- MOLLUSUM CONTAGIOSUM (1)
- mood changes (1)
- mood swings (1)
- motivation (1)
- motor disabilities (1)
- motor neurone disease (1)
- mouth (1)
- mouth ulcers (3)
- mouth washes (1)
- moving tract (1)
- MRI (5)
- multibacillary (1)
- multiple myeloma (2)
- Multiple sclerosis (1)
- mumps (2)
- Murphy Sign (1)
- muscle (3)
- muscle relaxant (1)
- muscle relaxant (6)
- muscle spasm (1)
- Muscle Tension Dysphonia (1)
- muscle weakness (1)
- music therapy (1)
- mutate (1)
- myasthenia gravis (1)
- mycobacterium leprae (1)
- Myelin (1)
- myocarditis (1)
- narrowed disc space (1)
- narrowed foramina (1)
- narrowing of artery (1)
- narrowing of bronchi (1)
- nasal congestion (1)
- nasal packing (1)
- nasal polyp (1)
- nasal spray (1)
- Nasopharyngeal cancer (2)
- nasopharynx (1)
- natural (1)
- nausea (5)
- neck collars (1)
- neck rigidity. (1)
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (1)
- NEPHROTIC SYNDROME (1)
- nerve cells (1)
- nerve compression (1)
- nerve conduction test (1)
- neurological deficit (1)
- Neurological Disorders (1)
- neurotransmission (1)
- new bone (1)
- new drugs (1)
- niacin (1)
- Night Blindness (1)
- nitrosamines (1)
- Nits on scalp (1)
- no cure (1)
- no menstruation (1)
- no petechiae (1)
- nocturia (4)
- non-paralytic (1)
- non-small cell (1)
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (1)
- nose (1)
- nosebleed (2)
- NSAID (1)
- NSAIDS (3)
- numbness (1)
- Obesity (5)
- Obesity.frequent thirst (1)
- obstruction (1)
- obstruction to air flow (1)
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (1)
- odor (1)
- older adults (1)
- olecranon bursitis (1)
- open angle glaucoma (1)
- open sores (1)
- optic nerve (1)
- or penis (1)
- oral (1)
- oral diabetic medicine (1)
- oral hygience (1)
- orchitis (2)
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta (1)
- osteomalacia (1)
- Osteomyelitis (1)
- osteophytes (1)
- osteoporosis (4)
- otitis externa (1)
- otitis media (3)
- Ovarian cancer (2)
- Ovarian torsion (1)
- overactivity (1)
- overflow (1)
- overweight (1)
- oxalates (1)
- P.falciparium (1)
- P.malariae (1)
- P.ovale (1)
- P.vivax (1)
- pain (25)
- painful (3)
- painful fallopian tubes (1)
- painful menstruation (1)
- painful swollen parotid glands (1)
- painful urination (1)
- painkillers (10)
- palms (1)
- pancreatic cancer (1)
- pancreatitis (4)
- panic attacks (1)
- Papanicolaou tests Pap smear (1)
- paralysis (2)
- paralytic (1)
- parasite (1)
- parasitic (1)
- Parkinson (1)
- paromyxovirus (1)
- Paronychia (1)
- partial (1)
- paucibacillary (1)
- PECOMA (1)
- Pediculosis (1)
- peduncle (1)
- pelvic inflammatory disease (3)
- pelvic pain (2)
- pelvis (1)
- Penicillin (1)
- penile implants (1)
- penile injection (1)
- penis (2)
- peptic ulcer (1)
- perforation (1)
- Pericarditis (1)
- peritonitis (1)
- Perivascular epithelioid cell (1)
- permanent disability (1)
- Permethrin 1% cream rinse (1)
- perpheral neuropathy (1)
- persistant cold (1)
- persistent pain (1)
- pessaries (1)
- petit mal (1)
- Phalen's test (1)
- phenytoin (1)
- phlebectomy (1)
- phlebitis (1)
- phlegm (1)
- photodermatitis (2)
- phototherapy (1)
- physiotherapy (7)
- physiotheray (1)
- PID (2)
- pigmentation (1)
- piles (2)
- pimples (1)
- pityriasis capitis (1)
- Pityriasis Rosea (1)
- plane (1)
- plantar (1)
- plantar fascilitis (1)
- plaque (1)
- plasma cell (1)
- plasmapheresis (1)
- Plasmodium (1)
- Pleural Effusion (1)
- pleurodesis (2)
- pneumococcus (2)
- pneumonia (2)
- Pneumothorax (1)
- polio virus (1)
- Poliomyelitis (1)
- pollen (2)
- Polycystic kidney disease (1)
- polycystic ovarian syndrome (1)
- polycystic ovary (2)
- polyps (3)
- poor blood circulation (1)
- poor coordination (1)
- poor drainage (1)
- poor healing of skin (1)
- porphyria (1)
- post-herpetic neuralgia (1)
- Postmenopausal bleeding (1)
- pregnancy (7)
- preinvasive (1)
- Premature (1)
- Premenstrual syndrome (1)
- prepuce (1)
- preserved food (2)
- pressure and posture (1)
- pressure change (1)
- pressure on nearby organs (1)
- Prickly Heat (1)
- prickly sensation (1)
- Primary (3)
- primary health care (1)
- probe (1)
- proctocolectomy (1)
- progressive disease (1)
- prolapsed disc (1)
- prolapsed intervertebral disc (1)
- prostate (6)
- prostate cancer (1)
- prostatic fluid test. bacteria culture (1)
- Prostatitis (1)
- Protease inhibitors (1)
- protozoan (1)
- pruritus (1)
- pseudocysts (1)
- pseudomembraous enterocolitis (1)
- pseudomonas (1)
- psoriasis (1)
- psychological factor (1)
- psychological suffering (1)
- Pterygium (1)
- puberty (1)
- pulmonary embolism (1)
- purpura (1)
- pustular (2)
- pustule (1)
- pyloric stenosis (1)
- quality of life (1)
- quinines (1)
- radiation (4)
- radioactive iodine (1)
- radiofrequency ablation (1)
- radiotherapy (9)
- radiotherapy. (1)
- rare (1)
- rash (2)
- rashes and abrasions (1)
- Raynaud's Disease (1)
- rectum (1)
- recurrence (1)
- recurrent outbreaks (1)
- red (5)
- red eyes (2)
- red scaly patches (1)
- redness (2)
- reduced oxygen (1)
- reflex mechanism (1)
- regenerated cells (1)
- regenerated tissue (1)
- region (1)
- regional enteritis (1)
- Regular checkups (1)
- rehyration (1)
- reiki (1)
- relax (2)
- relaxation (1)
- relaxation techniques (1)
- renal failure (1)
- renal stones (1)
- reorganisation (1)
- rest (12)
- rest tremors (2)
- rest voice (1)
- retention of urine (1)
- retina (1)
- retinal detachment (1)
- Retinitis pigmentosa (1)
- Reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors (1)
- Reye's syndrome (1)
- rheumatoid arthritis (1)
- rhinitis (1)
- rice water diarrhoea (1)
- rifampicin (1)
- rigidity (1)
- rigors (1)
- rose spots (1)
- roseala infantum (1)
- rotablation (1)
- rotator cuff injuries (1)
- rubber band (1)
- rubella (1)
- rule of nines (1)
- runny nose (2)
- sad (1)
- Salivary Gland cancer (1)
- salivary glands (1)
- Salmonella typhi (1)
- Salpingitis (1)
- Sarcoptes Scabiei (1)
- scabicides (1)
- Scabies (1)
- Scalds (1)
- scarlet fever (2)
- schizophrenia (1)
- sciatic nerve (1)
- sciatica (3)
- sclerotherapy (1)
- scoliosis (1)
- scratch marks (1)
- scratching (1)
- scurvy (1)
- sebaceous glands (2)
- seborrheic (1)
- secondary (5)
- seizures (1)
- semen.PSA (1)
- sentinel pile (1)
- septic arthritis (1)
- septicemia (1)
- severe and prolonged joint pains (1)
- Sex linkage (1)
- sexual activity (1)
- sexual contact (1)
- sexual exposure (1)
- Sexual Health (1)
- sexually transmitted disease (9)
- shampoo (1)
- sharp object (1)
- shigella (1)
- shingles (1)
- shivering (1)
- shock (1)
- Shoulder Xray (1)
- shunt (1)
- silent killer (1)
- silvadene (1)
- simple guide (2)
- simple skin care (1)
- single (1)
- sinus blockage (1)
- sinus washout (1)
- sinuses (1)
- sinusitis (2)
- skin (13)
- skin disease (1)
- skin Polyp (1)
- skin rash (1)
- Skin scrapings (1)
- skin tags (1)
- skin trophi (1)
- sleeping sickness (1)
- slipped disc (1)
- slow development (1)
- slow movement (1)
- slow urine flow (1)
- small cell (1)
- small papules (1)
- Small red bites (1)
- small vesicle (1)
- smoking (12)
- sneezing (2)
- snoring (2)
- soaps (1)
- socks (1)
- sodium valproate (1)
- soles (1)
- sore throat (4)
- sorethroat (1)
- Spasmodic (1)
- spasticity (1)
- spectacles (1)
- speech (1)
- speech loss (1)
- spine (1)
- Spine Xray (2)
- spleen (1)
- sponging (1)
- Spontaneous (1)
- spontaneous abortion (1)
- spore forming bacterium (1)
- spread (1)
- squamous cell carcinoma (1)
- staphalococcus aureus (1)
- staphylococci (1)
- staphylococcus aureus (1)
- statins (1)
- STD (2)
- stem cells (3)
- stent (1)
- stepladder fever (1)
- steroid (2)
- Steroid or immunosuppressive drugs (1)
- steroids (3)
- stiffness (3)
- stinger (1)
- stitching (1)
- stomach cancer (1)
- stomach inflammation (1)
- Stomatitis (1)
- stones (1)
- stool blood test (2)
- stool softener (1)
- stools (1)
- stop itch and pain (1)
- strangulated hernia (1)
- streptococci (1)
- streptococcus (1)
- stress (14)
- stridor (1)
- stripping of veins (1)
- stroke (5)
- stye (1)
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (1)
- subclinical (1)
- suicide (1)
- sulfasalazine (2)
- sulphonamides (1)
- sun (1)
- sun exposure (2)
- superficial (1)
- superficial linear tear (1)
- supranuclear (1)
- sur (1)
- surgery (33)
- surgery. (1)
- surgical coning of cervix (1)
- surgical resection (1)
- sweat glands (1)
- sweet urine (1)
- swelling (6)
- swelling in abdomen (1)
- swollen blood vessels (1)
- swollen glands behind ears and neck (1)
- sympathectomy (1)
- symptomatic treatment (1)
- syncope (1)
- Syphilis (1)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosis (1)
- systolic (1)
- tachycardia (1)
- tamoxifen (1)
- tears (1)
- telbivudine (1)
- temperature change (2)
- tender (1)
- tennis elbow (2)
- Tenosynovitis (1)
- tension (2)
- Tertiary (1)
- testicular pain (1)
- Testicular torsion (1)
- testosterone (1)
- tetanus (1)
- tetanus toxoid vaccine. Triple Antigen (1)
- tetracycline (2)
- thalassaemia (1)
- Thalassemia (1)
- thenar muscle wasting (1)
- Threadmill (2)
- threadworms (2)
- thymectomy (1)
- thymus (1)
- thyroid nodules (2)
- thyroid scan (1)
- thyroxine (1)
- tic (1)
- tinnitus (4)
- tinnitus. (1)
- tiredness (1)
- tissue damage (1)
- toe nails (1)
- tonsils (1)
- tooth discoloration (1)
- toothache (1)
- torsion (1)
- tracheostomy (2)
- track (1)
- traction (1)
- tranexamic acid (1)
- Transient ischaemic attack(TIA) (1)
- trauma (2)
- Treponema pallidum (1)
- Trichomonas vaginalis (1)
- trichomoniasis (1)
- trigeminal nerve (1)
- Trigeminal Neuralgia (1)
- trigger finger (1)
- trigger points (2)
- triggers (2)
- triglycerides (1)
- trimesters (1)
- tropical sprue (1)
- trypanosomes (1)
- tumour (1)
- Turner Syndrome (1)
- TURP (1)
- tying (1)
- Type 1 (1)
- Type 2 (1)
- typhoid carrier (1)
- Typhoid Fever (1)
- ueteric stones (1)
- Ulcerative Colitis (1)
- ulcers (2)
- ultrasound (4)
- ulttasound (1)
- UNDESCENDED TESTES (1)
- unknown cause (1)
- unwashed hands (1)
- urate crystals (1)
- ureteric colic (1)
- urethitis (1)
- Urethritis (1)
- urge (1)
- urgency (1)
- uric acid (1)
- uric aid (1)
- urinary incontinence (1)
- Urinary stones (1)
- Urinary Tract infection (1)
- urine problem (1)
- urine test (3)
- urostomy (1)
- urticaria (2)
- uterine ablation (1)
- uterine causes (1)
- Uterine Fibroids (1)
- uterine prolapse (1)
- uterus prolapse (1)
- UV light (1)
- uvea (1)
- uveitis (2)
- vaccine (2)
- vagina (2)
- vagina cancer (1)
- vaginal cancer (1)
- vaginal changes (1)
- vaginal discharge (1)
- vaginal douche (1)
- vaginal soreness (1)
- varicella vaccine (1)
- varicella-zoster virus (1)
- Varicose Veins (1)
- vasomotor rhinitis (1)
- vegetarian (1)
- venogram (1)
- venous stasis (1)
- vermiform appendix (1)
- vertigo (2)
- vertigo. (1)
- vesicovaginal fistula (1)
- Viagra (1)
- Vibrio cholorae (1)
- Vincent's Angina (1)
- viral (12)
- viral infection (2)
- viral infections (1)
- virus (3)
- viruses (1)
- vision loss (2)
- Vitamin A analogues (1)
- Vitamin A Deficiency (1)
- vitamin B1 deficiency (1)
- Vitamin B12 (1)
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency (1)
- Vitamin B2 Deficiency (1)
- vitamin B3 deficiency (1)
- vitamin B5 deficiency (1)
- Vitamin B6 Deficiency (1)
- vitamin B7 deficiency (1)
- Vitamin Bs (1)
- vitamin C deficiency (1)
- Vitamin D (1)
- Vitamin E Deficiency (1)
- vitamin K (1)
- Vitiligo (1)
- vitrectomy (1)
- vocal cord cyst (1)
- vocal cord nodule (1)
- vocal cord polyp (1)
- vocal cords (1)
- vocal paralysis (1)
- voice change (1)
- vomiting (5)
- vulva (1)
- Vulvitis (1)
- wafarin (1)
- walking (1)
- warm water (1)
- warmth (1)
- warts (1)
- wash hands (1)
- wash with water (1)
- wasps (1)
- wax (1)
- weak immune system (1)
- wear and tear (1)
- webs toes of foot (1)
- weight loss (7)
- Whooping cough (1)
- Wickham's striae (1)
- Widal test (1)
- wigs (1)
- wounds (1)
- wrist splintage (1)
- wrists (1)
- X-rays (3)
- xeroderma pigmentosa (2)
- yellow fever (1)
- yellow-green vaginal discharge (1)
- yoga (1)
- young child (1)




