A Simple Guide to Liver Cancer
----------------
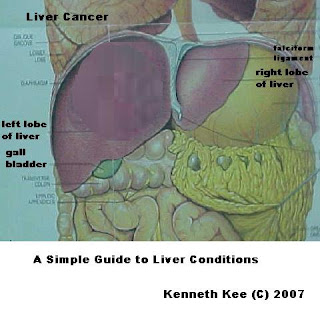
What is Liver Cancer?
---------------
Liver Cancer develops when the liver cells undergo abnormal changes to form cancer cells.
Most Primary cancer of the liver begins as mutated hepatocytes(liver cells).
Secondary cancer of the liver is due to spread from the stomach, colon, breast, lungs, ovaries etc
What is the incidence of Liver Cancer?
----------------------------------------------
Liver cancer is one of the most common cancer.
It occurs in men more than women.
It is more common in the 40s and 50s age groups.
What are the Risk Factors of Liver Cancer?
--------------------------------------------------
The main risk factor for liver cancer is
1.Hepatitis B infection.
Other important risk factors include
2.Hepatitis C infection
3.alcoholic liver disease (disease of the liver caused by heavy alcohol consumption).
4.family history of liver cancer
5.Chemicals exposures such as nitrites,solvents, hydrocarbons,viny chloride
6.poisons (e.g. aflatoxin present in some spoilt or mouldy peanuts).
7.inherited liver diseases (alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency)
8.Drug abuse eg heroin
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Liver Cancer?
------------------------------------------------------------
During the early stages, most people with liver cancer do not show any signs or symptoms.
Signs and symptoms, when they do appear, include:
1.loss of appetite and weight
2.discomfort or swelling in the upper part of the abdomen on the right side
3.weakness and fatigue
4.nausea and vomiting
5.jaundice - yellowness of the skin and eyes
6.dark color urine
7.Persistent or swinging fever
How is the Diagnosis of Liver Cancer confirmed?
--------------------------------------------------------
1. full medical history especially history of Hepatitis B and alcohol
2. full examination especially of the liver
3.an ultrasound scan of the liver and gallbladder, if possible the whole abdomen.
4.CT scan or MRI of the liver and surrounding tissues
5.blood tests (a protein present in blood called the alpha- fetoprotein or AFP may be found to be raised in liver cancer)
6.needle liver biopsy into the liver swelling as detected by ultrasound or MRI (to confirm the liver cancer).
With the diagnosis confirmed, the doctor will proceed with further tests to find out how advanced the liver cancer is. This will help the doctor to plan the treatment.
What is the Treatment of Liver Cancer?
---------------------------------------------
As in all cancers, treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy.
In Liver cancer percutaneous ethanol (alcohol) injection is injected directly into the tumour, by means of a small needle, to kill the cancerous cells.
Liver transplant can also be carried out in selected cases where the size of the cancer is not too massive but surgery is not feasible due to the patient's limited liver reserve(provided a suitable liver donor can be found).
Treatment depends on the the stage of the cancer as well as health of the affected person.
The goal of treatment is complete cure.
However, where this is not possible, treatment is aimed at
preventing the tumour from spreading or growing.
Helping to eliminate uncomfortable symptoms is also an important aspect of liver cancer treatment.
How to Protect yourself from Liver Cancer?
---------------------------------------------------
Prevention from getting liver cancer is by taking steps to reduce your risk factors.
1. Reduce your risk of Hepatitis B by getting vaccinated. The Hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective.
Both Hepatitis B and C are spread through infected blood or sexual fluids as well as intravenous drug abuse. It is therefore important to avoid activities that put you at risk:
2.Avoid multiple sex partners and having sex with commercial sex workers, strangers or anyone with multiple sex partners.
3.Do not abuse drugs or share injection needles.
4.Never share personal items like razors, toothbrushes or other items that may cause breaks in the skin.
5.Visit only reliable operators for ear/body piercing, tattooing or acupuncture.
6.It is also important that you limit your consumption of alcohol as excessive drinking can give rise to liver disease and increase your risk of liver cancer.
The liver is one of the largest and most important organs in your body. It performs many essential functions including:
making and storing of essential nutrients
making important hormones and enzymes
breaking down harmful substances.
Do not abuse Your LIVER by excessive drinking or taking drugs!
----------------
What is Liver Cancer?
---------------
Liver Cancer develops when the liver cells undergo abnormal changes to form cancer cells.
Most Primary cancer of the liver begins as mutated hepatocytes(liver cells).
Secondary cancer of the liver is due to spread from the stomach, colon, breast, lungs, ovaries etc
What is the incidence of Liver Cancer?
----------------------------------------------
Liver cancer is one of the most common cancer.
It occurs in men more than women.
It is more common in the 40s and 50s age groups.
What are the Risk Factors of Liver Cancer?
--------------------------------------------------
The main risk factor for liver cancer is
1.Hepatitis B infection.
Other important risk factors include
2.Hepatitis C infection
3.alcoholic liver disease (disease of the liver caused by heavy alcohol consumption).
4.family history of liver cancer
5.Chemicals exposures such as nitrites,solvents, hydrocarbons,viny chloride
6.poisons (e.g. aflatoxin present in some spoilt or mouldy peanuts).
7.inherited liver diseases (alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency)
8.Drug abuse eg heroin
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Liver Cancer?
------------------------------------------------------------
During the early stages, most people with liver cancer do not show any signs or symptoms.
Signs and symptoms, when they do appear, include:
1.loss of appetite and weight
2.discomfort or swelling in the upper part of the abdomen on the right side
3.weakness and fatigue
4.nausea and vomiting
5.jaundice - yellowness of the skin and eyes
6.dark color urine
7.Persistent or swinging fever
How is the Diagnosis of Liver Cancer confirmed?
--------------------------------------------------------
1. full medical history especially history of Hepatitis B and alcohol
2. full examination especially of the liver
3.an ultrasound scan of the liver and gallbladder, if possible the whole abdomen.
4.CT scan or MRI of the liver and surrounding tissues
5.blood tests (a protein present in blood called the alpha- fetoprotein or AFP may be found to be raised in liver cancer)
6.needle liver biopsy into the liver swelling as detected by ultrasound or MRI (to confirm the liver cancer).
With the diagnosis confirmed, the doctor will proceed with further tests to find out how advanced the liver cancer is. This will help the doctor to plan the treatment.
What is the Treatment of Liver Cancer?
---------------------------------------------
As in all cancers, treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy.
In Liver cancer percutaneous ethanol (alcohol) injection is injected directly into the tumour, by means of a small needle, to kill the cancerous cells.
Liver transplant can also be carried out in selected cases where the size of the cancer is not too massive but surgery is not feasible due to the patient's limited liver reserve(provided a suitable liver donor can be found).
Treatment depends on the the stage of the cancer as well as health of the affected person.
The goal of treatment is complete cure.
However, where this is not possible, treatment is aimed at
preventing the tumour from spreading or growing.
Helping to eliminate uncomfortable symptoms is also an important aspect of liver cancer treatment.
How to Protect yourself from Liver Cancer?
---------------------------------------------------
Prevention from getting liver cancer is by taking steps to reduce your risk factors.
1. Reduce your risk of Hepatitis B by getting vaccinated. The Hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective.
Both Hepatitis B and C are spread through infected blood or sexual fluids as well as intravenous drug abuse. It is therefore important to avoid activities that put you at risk:
2.Avoid multiple sex partners and having sex with commercial sex workers, strangers or anyone with multiple sex partners.
3.Do not abuse drugs or share injection needles.
4.Never share personal items like razors, toothbrushes or other items that may cause breaks in the skin.
5.Visit only reliable operators for ear/body piercing, tattooing or acupuncture.
6.It is also important that you limit your consumption of alcohol as excessive drinking can give rise to liver disease and increase your risk of liver cancer.
The liver is one of the largest and most important organs in your body. It performs many essential functions including:
making and storing of essential nutrients
making important hormones and enzymes
breaking down harmful substances.
Do not abuse Your LIVER by excessive drinking or taking drugs!