[caption id="" align="alignright" width="300" caption="Image via Wikipedia"] [/caption]
[/caption]
DOC HOW DO I KNOW WHETHER MY STOOL IS NORMAL
Actually many people do not know the definition of diarrhea.
They define the word diarrhea as watery stools where in fact the word diarrhea means any stools which are softer or more frequent than normal.
The researchers at the Bristol University have come out with a scale which is called the Bristol Stool Scale.
According to the Bristol Stool Scale, the seven types of stools
are:
1.Type 1: Separate hard lumps like nuts
2.Type 2: Sausage shaped but lumpy
3.Type 3: like a Sausage but with cracks on its surface
4.Type 4: like a Sausage or snake, smooth and soft
5.Type 5: soft blobs with clear cut edges
6.Type 6: Fluffy pieces with ragged edges, a mushy stool
7.Type 7: Watery, no solid pieces. Entirely liquid.
Type 1 and 2 indicate constipation while type 5-7 indicate diarrhea. Type 3 and 4 are considered ideal stools because they are the easiest to pass.
Avoidance of constipation include:
1. Increase in daily fiber intake to at least 15gm (eg. 1 bowl of bran cereal for breakfast),
fruits and vegetables).
Fibre increases the bulk of the stool allowing easy passage of stools through the large
intestine.
2. Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day (2 liters). Water reduces the hardness of stools.
3. Regular exercises at least 2-3 times a day especially after meals. Exercise will enhance
intestinal movement.
4. Allow a distraction free period of 15 min a day for bowel movement. The strongest
intestinal movement occurs after breakfast.
5. Do not ignore or suppress the urge to pass bowel movement. This may impair the
sensation to detect initiation of bowel movement leading to constipation.
Avoidance of diarrhea include:
1.washing your hands thoroughly for 20 seconds after using the bathroom or changing diapers
2.washing your hands thoroughly for 20 seconds before eating
3.disinfecting contaminated surfaces such as counter tops and baby changing stations
4.Avoid eating or drinking foods or liquids that might be contaminated
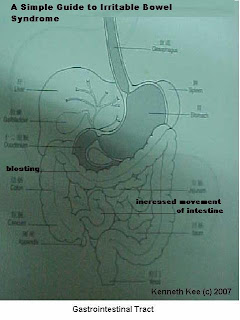
5.Avoid rapid intestinal movement from stress, irritable bowel syndrome
Please read my blogs on constipation and diarrhea
 [/caption]
[/caption]DOC HOW DO I KNOW WHETHER MY STOOL IS NORMAL
Actually many people do not know the definition of diarrhea.
They define the word diarrhea as watery stools where in fact the word diarrhea means any stools which are softer or more frequent than normal.
The researchers at the Bristol University have come out with a scale which is called the Bristol Stool Scale.
According to the Bristol Stool Scale, the seven types of stools
are:
1.Type 1: Separate hard lumps like nuts
2.Type 2: Sausage shaped but lumpy
3.Type 3: like a Sausage but with cracks on its surface
4.Type 4: like a Sausage or snake, smooth and soft
5.Type 5: soft blobs with clear cut edges
6.Type 6: Fluffy pieces with ragged edges, a mushy stool
7.Type 7: Watery, no solid pieces. Entirely liquid.
Type 1 and 2 indicate constipation while type 5-7 indicate diarrhea. Type 3 and 4 are considered ideal stools because they are the easiest to pass.
Avoidance of constipation include:
1. Increase in daily fiber intake to at least 15gm (eg. 1 bowl of bran cereal for breakfast),
fruits and vegetables).
Fibre increases the bulk of the stool allowing easy passage of stools through the large
intestine.
2. Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day (2 liters). Water reduces the hardness of stools.
3. Regular exercises at least 2-3 times a day especially after meals. Exercise will enhance
intestinal movement.
4. Allow a distraction free period of 15 min a day for bowel movement. The strongest
intestinal movement occurs after breakfast.
5. Do not ignore or suppress the urge to pass bowel movement. This may impair the
sensation to detect initiation of bowel movement leading to constipation.
Avoidance of diarrhea include:
1.washing your hands thoroughly for 20 seconds after using the bathroom or changing diapers
2.washing your hands thoroughly for 20 seconds before eating
3.disinfecting contaminated surfaces such as counter tops and baby changing stations
4.Avoid eating or drinking foods or liquids that might be contaminated
5.Avoid rapid intestinal movement from stress, irritable bowel syndrome
Please read my blogs on constipation and diarrhea